110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SIRT1 通过无菌性松动中的 NF-κB 去乙酰化来调节金属纳米颗粒诱导的炎症反应
Authors Deng Z, Jin J, Wang Z, Wang Y, Gao Q, Zhao J
Received 14 October 2016
Accepted for publication 10 April 2017
Published 10 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3617—3636
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S124661
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
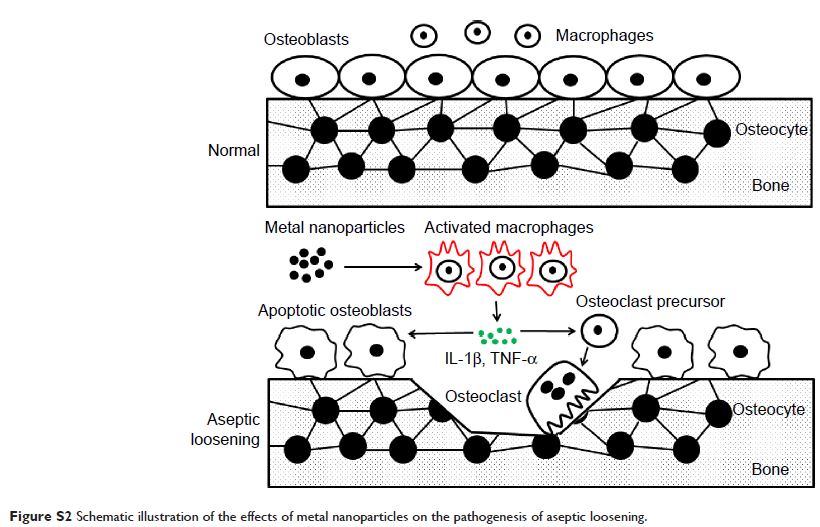
Abstract: Aseptic loosening is the most common cause of total hip arthroplasty
(THA) failure, and osteolysis induced by wear particles plays a major role in
aseptic loosening. Various pathways in multiple cell types contribute to the
pathogenesis of osteolysis, but the role of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), which can
regulate inflammatory responses through its deacetylation, has never been
investigated. We hypothesized that the downregulation of SIRT1 in macrophages
induced by metal nanoparticles was one of the reasons for osteolysis in THA
failure. In this study, the expression of SIRT1 was examined in macrophages
stimulated with metal nanoparticles from materials used in prosthetics and in
specimens from patients suffering from aseptic loosening. To address whether
SIRT1 downregulation triggers these inflammatory responses, the effects of the
SIRT1 activator resveratrol on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in
metal nanoparticle-stimulated macrophages were tested. The results demonstrated
that SIRT1 expression was significantly downregulated in metal
nanoparticle-stimulated macrophages and clinical specimens of prosthesis
loosening. Pharmacological activation of SIRT1 dramatically reduced the
particle-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines in vitro and osteolysis
in vivo. Furthermore, SIRT1 regulated particle-induced inflammatory responses
through nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) acetylation. Thus, the results of this
study suggest that SIRT1 plays a key role in metal nanoparticle-induced
inflammatory responses and that targeting the SIRT1 pathway may lead to novel
therapeutic approaches for the treatment of aseptic prosthesis loosening.
Keywords: metal nanoparticle, inflammatory
response, SIRT1, NF-κB, aseptic loosening