110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
HMGCS2 用于对行食管鳞状细胞癌切除手术的中国患者的预后进行预测的价值
Authors Tang H, Wu Y, Qin Y, Wang H, Jia Y, Yang S, Luo S, Wang Q
Received 17 January 2017
Accepted for publication 22 April 2017
Published 15 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2553—2560
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S132543
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Abstract: Despite a series of
attempts during the last decades, the prognosis of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (ESCC) remains poor. Different responses of individual tumors
encouraged us to look for valuable prognostic markers. As a key regulator
controlling the anabolic ketogenic pathway, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA
synthase 2 (HMGCS2 ) has been reported to play
a crucial role in colorectal cancer and prostate cancer. However, its
importance to ESCC has not been verified. Therefore, a large cohort
retrospective study was planned, to investigate the relationship between HMGCS2 expression
and ESCC prognosis. By adopting real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and
immunohistochemical (IHC) staining, HMGCS2 expression
was examined in tissues of 300 ESCC patients with complete resection. Besides,
the association between HMGCS2 protein expression and survival time was
evaluated through chi-square test and Kaplan–Meier analysis. With the use of
Cox-proportional hazards model, the prognostic impact of clinicopathologic
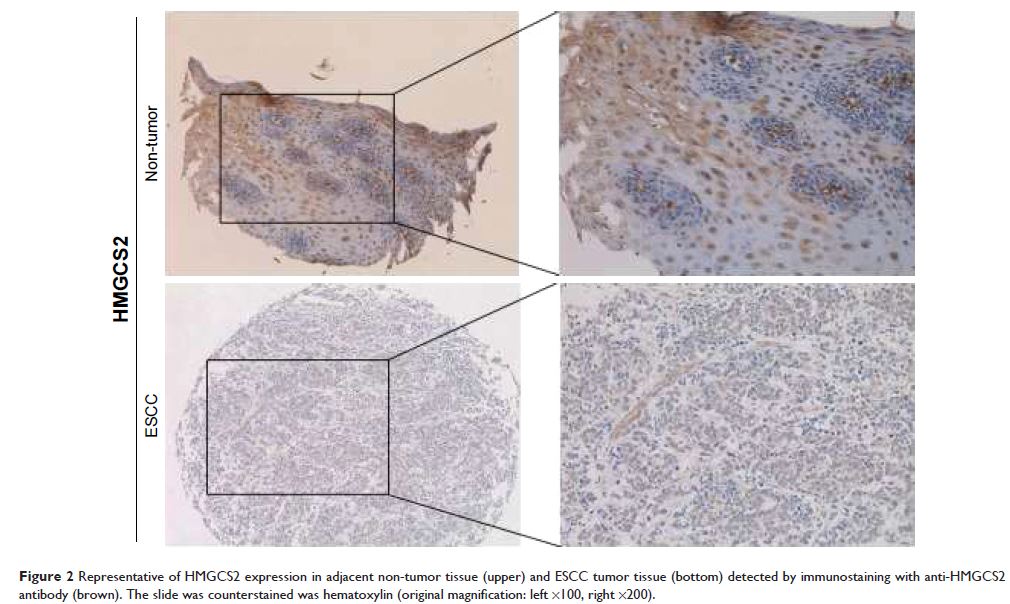
variables and biomarker expression was evaluated. Compared with their non-tumor
counterparts, HMGCS2 downregulation
occurred in 65.5% and 37.6% of primary ESCCs on the mRNA and protein levels (P <0.001), respectively. On the
protein level, HMGCS2 expression was associated with tumor cell differentiation
(P =0.003), pT status (P =0.006), and TNM stage (P =0.010). In the down-HMGCS2
expression group, the 5-year overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival
(RFS) are poorer than those in the normal expression group (19 months vs 24
months, P =0.002; 13 months vs 17 months, P =0.007,
respectively). According to the TNM stage, stratified analysis revealed that
its discernibility on RFS was only pronounced in patients with advanced
clinical stage (P =0.001). In addition,
multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that HMGCS2 expression was an
independent risk factor for RFS (P =0.032) instead of
OS (P =0.099). The findings of this
study provided the evidence that HMGSC2 represented a potential novel
prognostic biomarker for ESCC patients.
Keywords: HMGCS2, ESCC, prognosis, down-regulation, IHC, Chinese
Keywords: HMGCS2, ESCC, prognosis, down-regulation, IHC, Chinese