110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

顺铂 (Cisplatin) 耐药肺癌细胞衍生的外来体能够以核外 miR-100-5p 依赖方式增加受体细胞的顺铂耐药性
Authors Qin X, Yu S, Zhou L, Shi M, Hu Y, Xu X, Shen B, Liu S, Yan D, Feng J
Received 3 January 2017
Accepted for publication 3 April 2017
Published 15 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3721—3733
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131516
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
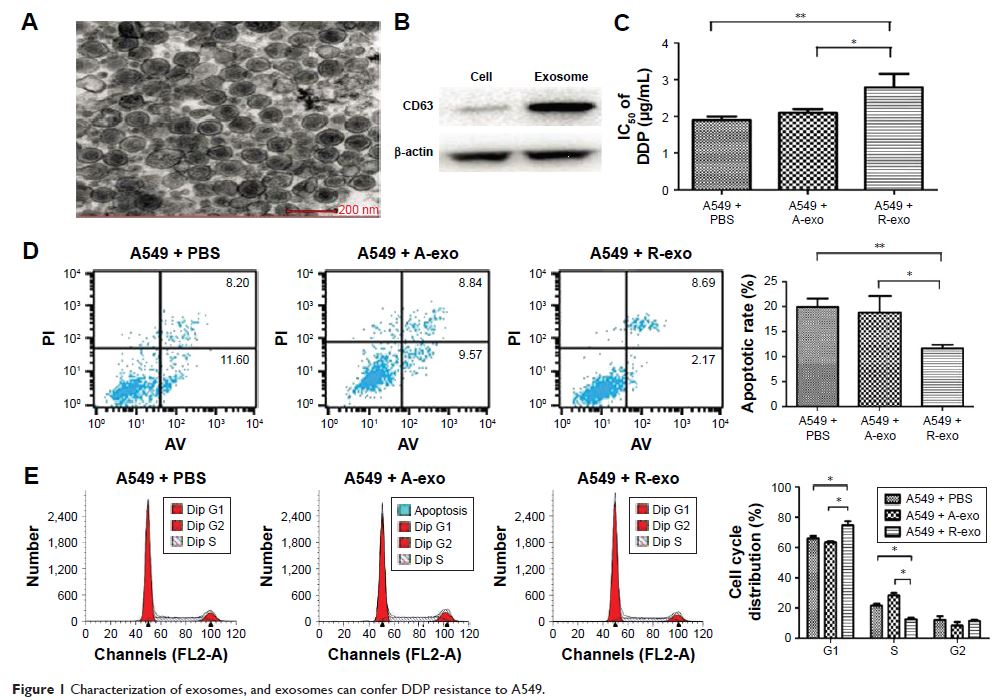
Abstract: Exosomes derived from lung cancer cells confer cisplatin (DDP)
resistance to other cancer cells. However, the underlying mechanism is still
unknown. A549 resistance to DDP (A549/DDP) was established. Microarray was used
to analyze microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles of A549 cells, A549/DDP cells,
A549 exosomes, and A549/DDP exosomes. There was a strong correlation of miRNA
profiles between exosomes and their maternal cells. A total of 11 miRNAs were
significantly upregulated both in A549/DDP cells compared with A549 cells and
in exosomes derived from A549/DDP cells in contrast to exosomes from A549
cells. A total of 31 downregulated miRNAs were also observed. miR-100–5p was
the most prominent decreased miRNA in DDP-resistant exosomes compared with the
corresponding sensitive ones. Downregulated miR-100–5p was proved to be
involved in DDP resistance in A549 cells, and mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR) expression was reverse regulated by miR-100–5p. Exosomes confer
recipient cells’ resistance to DDP in an exosomal miR-100–5p-dependent manner
with mTOR as its potential target both in vitro and in vivo. Exosomes from
DDP-resistant lung cancer cells A549 can alter other lung cancer cells’
sensitivity to DDP in exosomal miR-100–5p-dependent manner. Our study provides
new insights into the molecular mechanism of DDP resistance in lung cancer.
Keywords: lung cancer, cisplatin, exosome,
miR-100–5p, drug resistance