110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Anti-amyloid aggregation activity of novel carotenoids: implications for Alzheimer’s drug discovery
Authors Lakey-Beitia J, Doens D, Jagadeesh Kumar D, Murillo E, Fernández PL, Rao KS, Durant-Archibold AA
Received 14 February 2017
Accepted for publication 7 April 2017
Published 15 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 815—822
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S134605
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 6
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Walker
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia, affecting
approximately 33.5 million people worldwide. Aging is the main risk factor
associated with AD. Drug discovery based on nutraceutical molecules for
prevention and treatment of AD is a growing topic. In this sense, carotenoids
are phytochemicals present mainly in fruits and vegetables with reported
benefits for human health. In this research, the anti-amyloidogenic activity of
three carotenoids, cryptocapsin, cryptocapsin-5,6-epoxide, and zeaxanthin, was
assessed. Cryptocapsin showed the highest bioactivity, while
cryptocapsin-5,6-epoxide and zeaxanthin exhibited similar activity on
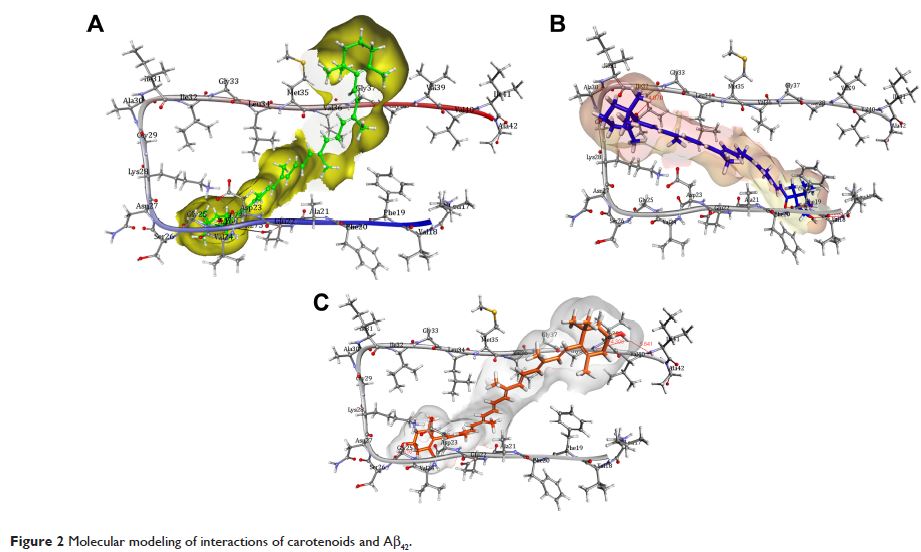
anti-aggregation assays. Molecular modeling analysis revealed that the
evaluated carotenoids might follow two mechanisms for inhibiting Aβ
aggregation: by preventing the formation of the fibril and through disruption
of the Aβ aggregates. Our studies provided evidence that cryptocapsin,
cryptocapsin-5,6-epoxide, and zeaxanthin have anti-amyloidogenic potential and
could be used for prevention and treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, aging,
anti-amyloidogenic activity, cryptocapsin, cryptocapsin-5,6-epoxide, zeaxanthin