110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

掺杂 IONP 的纳米粒子用于高效、NIR 控制的药物释放和组合肿瘤治疗
Authors Fu X, Wang X, Zhou S, Zhang Y
Received 31 May 2016
Accepted for publication 5 September 2016
Published 16 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3751—3766
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S113963
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
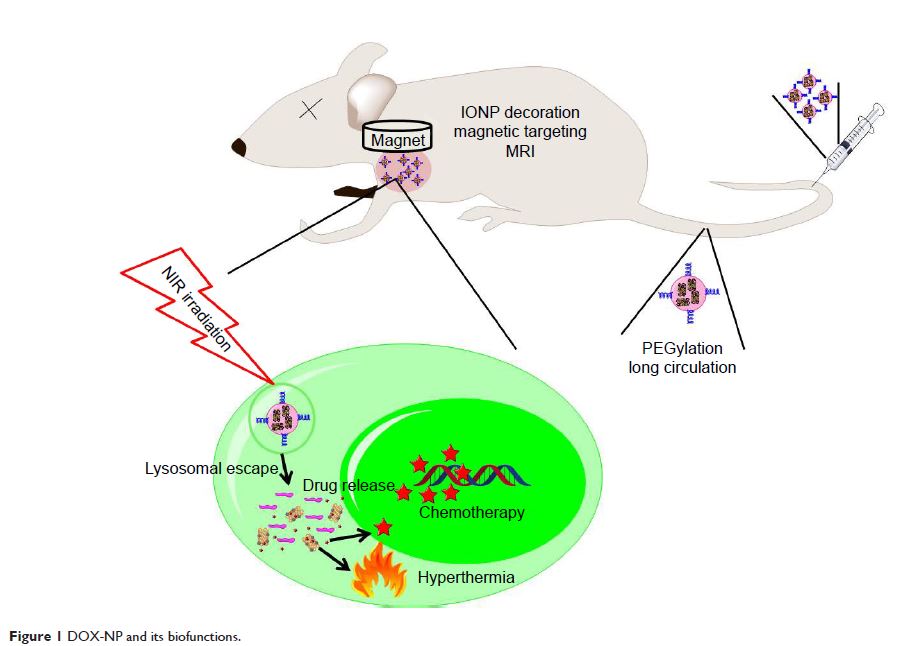
Abstract: Despite advances in controlled drug delivery, drug delivery systems
(DDSs) with controlled activated drug release and high spatial and temporal
resolution are still required. Theranostic nanomedicine is capable of
diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring the delivery and distribution of drug
molecules and has received growing interest. In this study, a near-infrared
light-controlled “off–on” DDS with magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic
targeting properties was developed using a hybrid nanoplatform (carbon
nanotubes [CNTs]-iron oxide nanoparticle). Doxorubicin (DOX) and distearoyl-sn -glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-PEG
were adsorbed onto CNTs-iron oxide nanoparticle, and then to avoid the
unexpected drug release during circulation, 1-myristyl alcohol was used to
encapsulate the CNTs–drug complex. Herein, multifunctional DOX-loaded
nanoparticles (NPs) with “off–on” state were developed. DOX-NPs showed an
obvious “off–on” effect (temperature increase, drug release) controlled by
near-infrared light in vitro and in vivo. In the in vivo and in vitro studies,
DOX-NPs exhibited excellent magnetic resonance imaging ability, magnetic
targeting property, high biosafety, and high antitumor combined therapeutic
efficacy (hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy). These results highlight the
great potential of DOX-NPs in the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: controlled drug
release, magnetic targeting, MRI, combination therapy