110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RNA 结合蛋白 HuR 通过将 miR-1 与长非编码 HOTAIR 进行竞争性结合来促进膀胱癌的发展
Authors Yu DP, Zhang C, Gui JQ
Received 18 January 2017
Accepted for publication 13 March 2017
Published 17 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2609—2619
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S132728
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Abstract: The elevated expressions of RNA-binding protein HuR and long noncoding
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) are observed in numerous cancers. And HuR
often exerts its promotive effects on tumorigenesis via binding to AU-rich
elements in target transcripts and thus regulating the expression of target
transcripts. However, the roles and related mechanisms of HuR/HOTAIR in bladder
cancer progression have never been formally tested. Here, we found that the
expression level of HuR was higher in clinical bladder cancer samples than in
normal adjacent samples, mirroring that of HOTAIR, and their expression showed
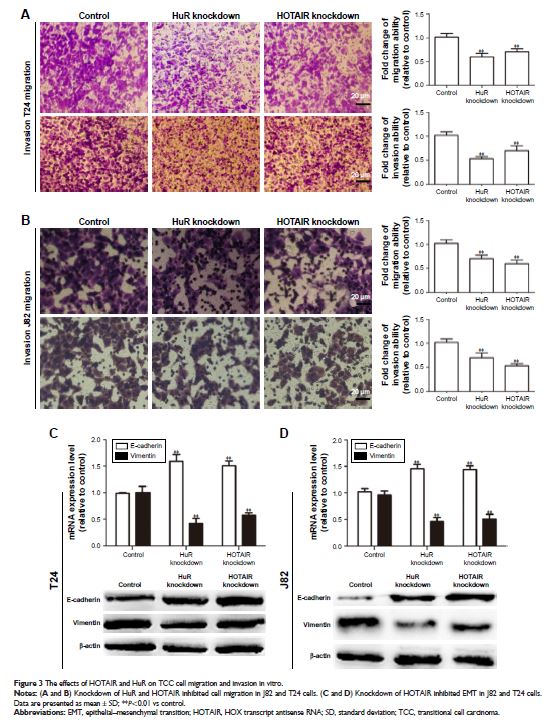
strong correlation. Knockdown of HuR/HOTAIR in bladder cancer inhibited cell
proliferation, migration, invasion, and promoted cell apoptosis. Notably, HuR
interacted and stabilized HOTAIR mRNA and knockdown of HuR decreased HOTAIR
expression. Additionally, HOTAIR was identified as a potential target of miR-1
in bladder cancer cells. Interestingly, overexpression of HOTAIR enhanced HuR
expression and increased cytoplasmic accumulation of HuR, thus enhancing HOTAIR
expression in turn. But mutation of miR-1 binding site in HOTAIR canceled the
effects of HOTAIR on HuR expression. Overall, we identified a regulatory loop between
HOTAIR and HuR during the progression of bladder cancer, which could be
exploited to curb bladder cancer progression.
Keywords: HuR, HOTAIR, bladder cancer, miR-1