110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

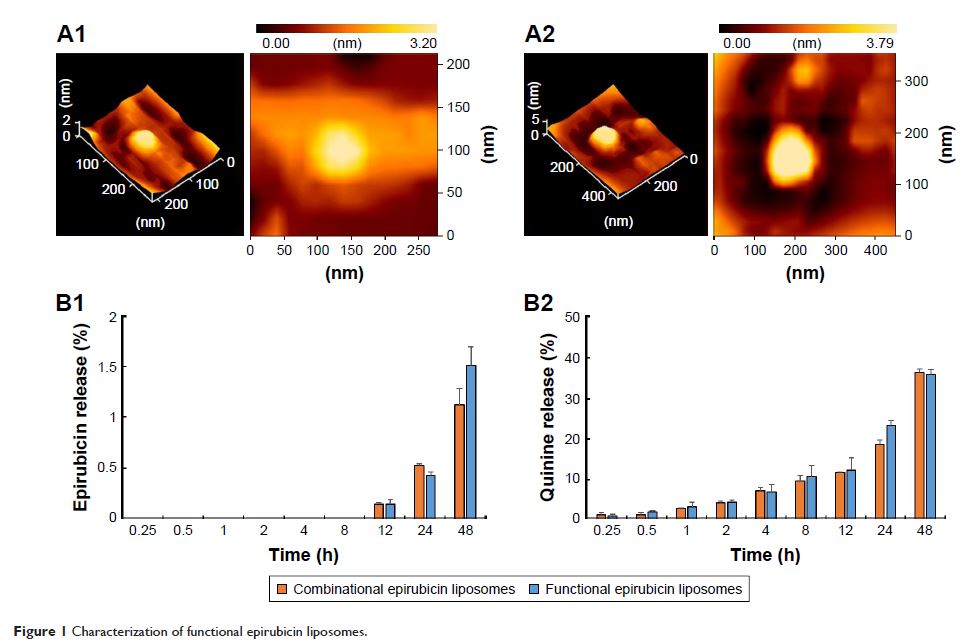
使用功能性表柔比星 (Epirubicin) 脂质体诱导难治性乳腺癌中的程序性死亡
Authors Liu L, Mu LM, Yan Y, Wu JS, Hu YJ, Bu YZ, Zhang JY, Liu R, Li XQ, Lu WL
Received 25 January 2017
Accepted for publication 18 April 2017
Published 1 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4163—4176
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S133194
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Currently, chemotherapy is less efficient in controlling the continued
development of breast cancer because it cannot eliminate extrinsic and
intrinsic refractory cancers. In this study, mitochondria were modified by
functional epirubicin liposomes to eliminate refractory cancers through
initiation of an apoptosis cascade. The efficacy and mechanism of epirubicin
liposomes were investigated on human breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
using flow cytometry, confocal microscopy, high-content screening system, in
vivo imaging system, and tumor inhibition in mice. Mechanistic studies revealed
that the liposomes could target the mitochondria, activate the apoptotic
enzymes caspase 8, 9, and 3, upregulate the proapoptotic protein Bax while
downregulating the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1, and induce the generation of
reactive oxygen species (ROS) through an apoptosis cascade. In xenografted mice
bearing breast cancer, the epirubicin liposomes demonstrated prolonged blood
circulation, significantly increased accumulation in tumor tissue, and robust
anticancer efficacy. This study demonstrated that functional epirubicin
liposomes could significantly induce programmed death of refractory breast cancer
by activating caspases and ROS-related apoptotic signaling pathways, in
addition to the direct killing effect of the anticancer drug itself. Thus, we
present a simple nanomedicine strategy to treat refractory breast cancer.
Keywords: mitochondria, drug delivery,
apoptosis, efficacy, signaling pathway