110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文已被撤回 — SUN1 沉默通过肺腺癌中的 G0/G1 期阻滞抑制细胞生长
Authors Huang W, Huang H, Wang L, Hu J, Song W
Received 22 December 2014
Accepted for publication 6 May 2015
Published 2 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2825—2833
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S79727
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
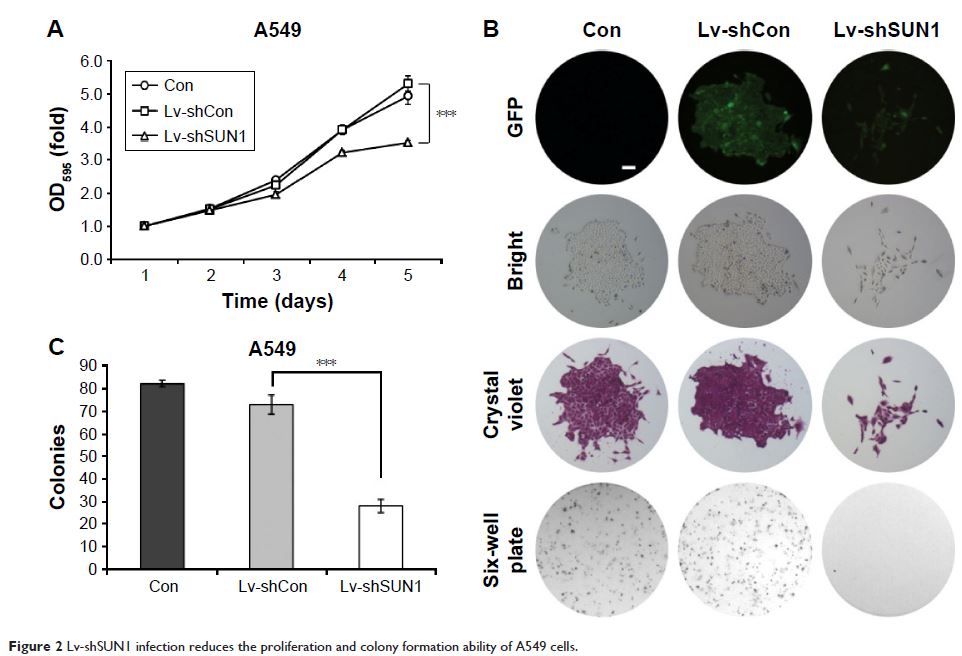
Methods: In this study, we first transduced the lentivirus delivering the short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against SUN1 to lung adenocarcinoma cells (A549 and 95D cells) with high efficiency. After lentivirus infection, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting were used to detect the expressions of SUN1 mRNA and protein. The cell proliferation and colony formation were detected by MTT assay and colony formation assay, respectively. The cell distribution in the cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: Both mRNA and protein levels of SUN1 were significantly decreased in A549 and 95D cells after lentivirus infection, as indicated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot. Next, we found that cell proliferation and colony formation were markedly reduced in SUN1 silenced cells. Moreover, suppression of SUN1 led to cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. Furthermore, Cyclin D1, CDK6, and CDK2 expressions were obviously reduced in A549 cells after SUN1 silencing.
Conclusion: These results suggest that SUN1 plays an essential role in proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro and may be used as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma in the future.
Keywords: SUN1, lung cancer, proliferation
作者现发声明撤回已发表的论文:
这篇文章已经在 OncoTargets and Therapy 主编的要求下被撤回。论文作者不能证实对照组慢病毒所携带的序列是 TTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTCTCGA GACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAATTTTT,因此他们决定收回论文,并再次进行实验以重新测试数据。
撤稿启事