110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

生物可降解和生物相容的阳离子聚合物通过提供微小 RNA-221/222 促进坐骨神经挤压后的神经再生
Authors Song J, Li X, Li Y, Che J, Li X, Zhao X, Chen Y, Zheng X, Yuan W
Received 11 January 2017
Accepted for publication 3 April 2017
Published 2 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4195—4208
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S132190
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: MicroRNA (miRNA) has great potential to treat a wide range of
illnesses by regulating the expression of eukaryotic genes. Biomaterials with
high transfection efficiency and low toxicity are needed to deliver miRNA to
target cells. In this study, a biodegradable and biocompatible cationic polymer
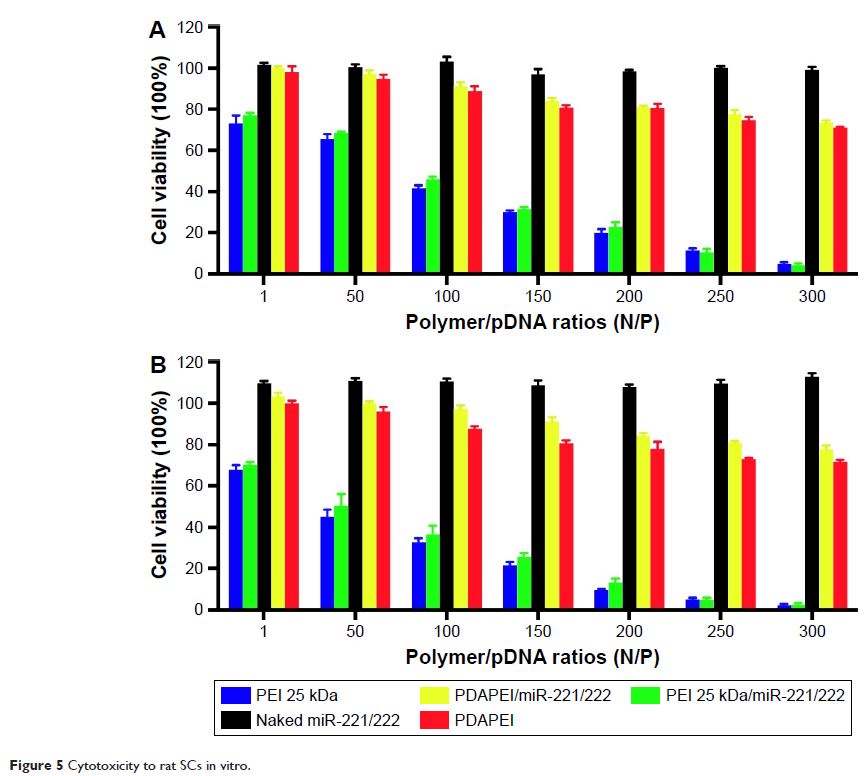
(PDAPEI) was synthetized from low molecular weight polyethyleneimine
(PEI1.8kDa) cross-linked with 2,6-pyridinedicarboxaldehyde. PDAPEI showed a
lower cytotoxicity and higher transfection efficiency than PEI25kDa in transfecting
miR-221/222 into rat Schwann cells (SCs). The upregulation of miR-221/222 in
SCs promoted the expression of nerve growth factor and myelin basic protein in
vitro. The mouse sciatic nerve crush injury model was used to evaluate the
effectiveness of PDAPEI/miR-221/222 complexes for nerve regeneration in vivo.
The results of electrophysiological tests, functional assessments, and
histological and immunohistochemistry analyses demonstrated that
PDAPEI/miR-221/222 complexes significantly promoted nerve regeneration after
sciatic nerve crush, specifically enhancing remyelination. All these results
show that the use of PDAPEI to deliver miR-221/222 may provide a safe
therapeutic means of treating nerve crush injury and may help to overcome the
barrier of biomaterial toxicity and low efficiency often encountered during
medical intervention.
Keywords: miR-221/222, PDAPEI, nerve
regeneration, remyelination