110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

分级 pH 响应纳米粒子用于增强细胞摄取和多柔比星 (doxorubicin) 的按需细胞内释放
Authors Chen WL, Li F, Tang Y, Yang SD, Li JZ, Yuan ZQ, Liu Y, Zhou XF, Liu C, Zhang XN
Received 8 December 2016
Accepted for publication 1 March 2017
Published 6 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4241—4256
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S129748
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
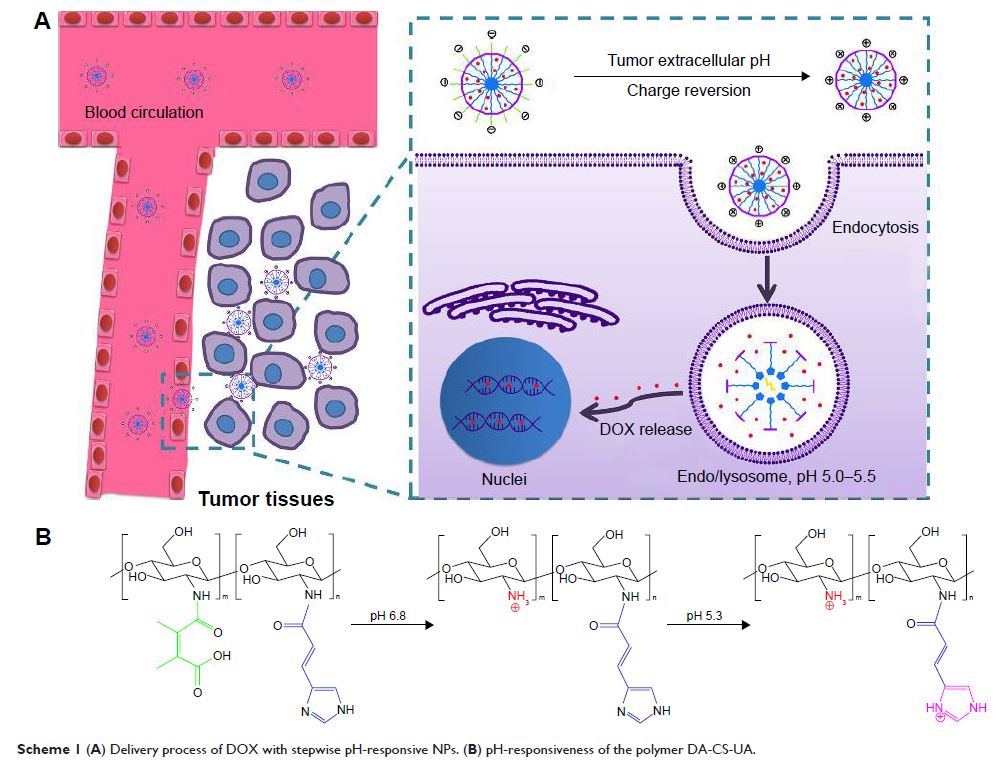
Abstract: Physicochemical properties, including particle size, zeta potential, and
drug release behavior, affect targeting efficiency, cellular uptake, and
antitumor effect of nanocarriers in a formulated drug-delivery system. In this
study, a novel stepwise pH-responsive nanodrug delivery system was developed to
efficiently deliver and significantly promote the therapeutic effect of
doxorubicin (DOX). The system comprised dimethylmaleic acid-chitosan-urocanic
acid and elicited stepwise responses to extracellular and intracellular pH. The
nanoparticles (NPs), which possessed negative surface charge under
physiological conditions and an appropriate nanosize, exhibited advantageous
stability during blood circulation and enhanced accumulation in tumor sites via
enhanced permeability and retention effect. The tumor cellular uptake of
DOX-loaded NPs was significantly promoted by the first-step pH response,
wherein surface charge reversion of NPs from negative to positive was triggered
by the slightly acidic tumor extracellular environment. After internalization
into tumor cells, the second-step pH response in endo/lysosome acidic
environment elicited the on-demand intracellular release of DOX from NPs,
thereby increasing cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Furthermore, stepwise
pH-responsive NPs showed enhanced antiproliferation effect and reduced systemic
side effect in vivo. Hence, the stepwise pH-responsive NPs provide a promising
strategy for efficient delivery of antitumor agents.
Keywords: stepwise pH-responsive, charge
reversal, on-demand drug release, efficient delivery