110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于口腔白色念珠菌 (Candida albicans ) 局部治疗、加载两性霉素 B 的 MPEG-PCL-g-PEI 胶束的制备、表征和评估
Authors Zhou L, Zhang P, Chen Z, Cai S, Jing T, Fan H, Mo F, Zhang J, Lin R
Received 9 October 2016
Accepted for publication 27 March 2017
Published 6 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4269—4283
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S124264
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Fatal Candida albicans infections in the mucosal system can
occur in association with immune-compromised diseases and dysbacteriosis.
Currently, amphotericin B (AmB) is considered to be the most effective
antibiotic in the treatment of C. albicans infections, but its clinical
application is limited by side effects and poor bioavailability. In order to
use AmB in the local treatment of oral C. albicans infections, AmB/MPEG-PCL-g-PEI
(monomethoxy poly(ethylene
glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-graft-polyethylenimine, MPP) micelles were
prepared. A series of characterizations were performed. The micelles allowed a
sustained in vitro release in both normal oral conditions (pH 6.8) and C. albicans infection conditions (pH 5.8). Then,
buccal tablets containing freeze-dried powder of AmB/MPP micelles were produced
by direct compression process and evaluated as regards to weight variation,
hardness, and friability. In vitro drug release of the buccal tablets was
measured in both the United States Pharmacopeia dissolution apparatus and the
dissolution rate test apparatus, which was previously designed for simulating
in vivo conditions of the oral cavity. The buccal tablets could sustainably
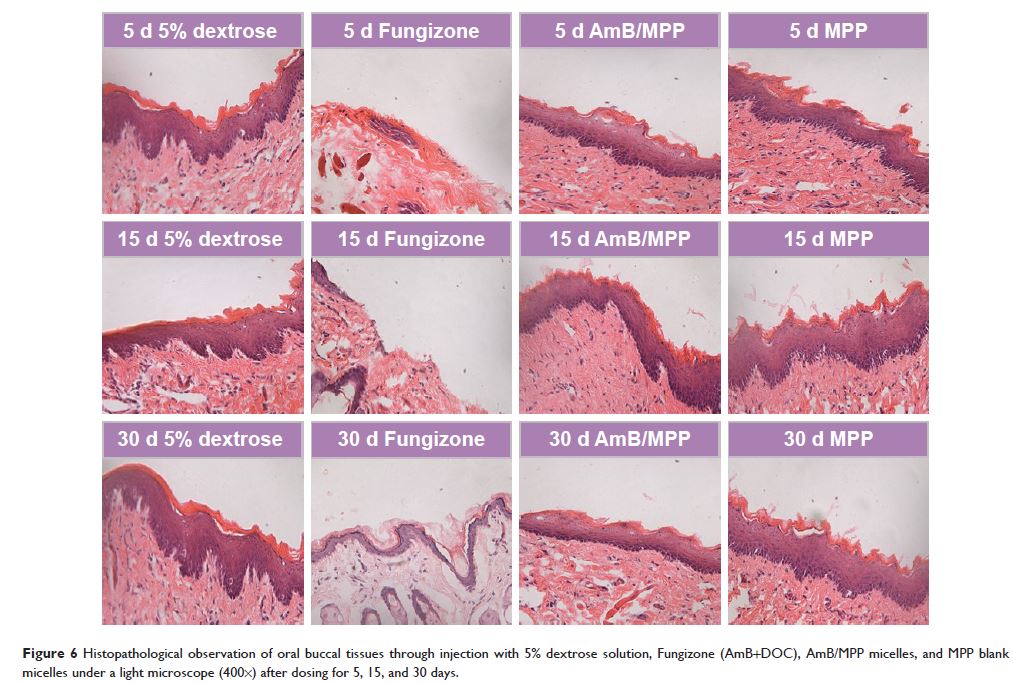
release within 8 h and meet the antifungal requirements. Regarding safety
assessment of AmB/MPP micelles, in vivo histopathological data showed no
irritation toward buccal mucosa of the rats in both optical microscopy and
ultrastructure observation of the tissues. MTT experiment proved that AmB/MPP
micelles reduced the cytotoxicity of AmB. The micelles delivered through the
gastrointestinal route were also found to be non-systemic toxicity by liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Furthermore, the antifungal action
of AmB/MPP micelles was evaluated. Although AmB/MPP had no obvious improvement
as compared to AmB alone in the antifungal effect on planktonic C. albicans , the micelles
significantly enhanced the antifungal activity against the biofilm state of C. albicans . Thus,
it was concluded that AmB/MPP micelles represent a promising novel drug
delivery system for the local treatment of oral C. albicans infections.
Keywords: amphotericin B, micelle, Candida albicans , safety
evaluation, buccal tablet, antifungal effect