110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Ti-GO-Ag 纳米复合材料: 含量水平对抗菌活性和细胞毒性的影响
Authors Jin J, Zhang L, Shi M, Zhang Y, Wang Q
Received 16 February 2017
Accepted for publication 17 April 2017
Published 7 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4209—4224
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S134843
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
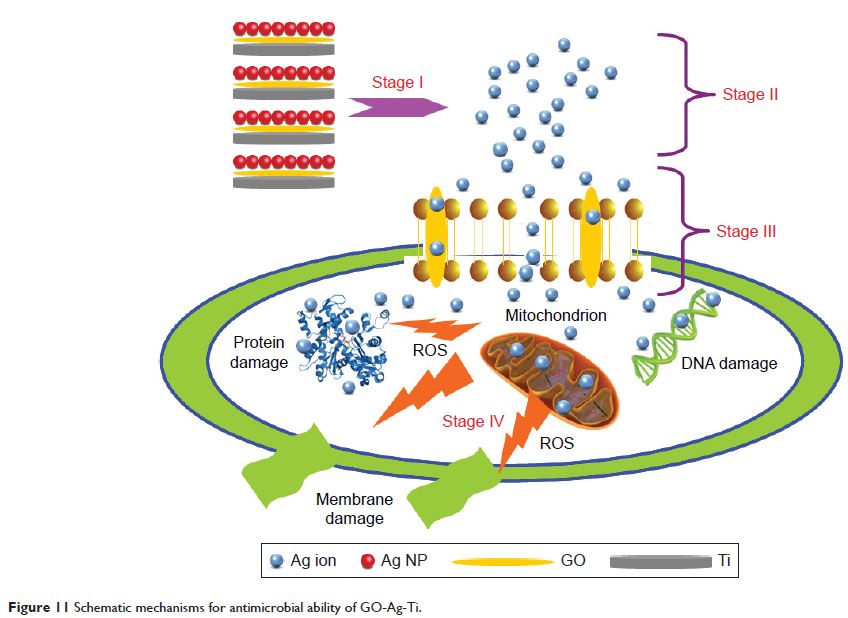
Abstract: Surface modification of titanium (Ti) implants are extensively studied
in order to obtain prominent biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity,
especially preventing implant-associated infection. In this study, Ti
substrates surface were modified by graphene oxide (GO) thin film and silver
(Ag) nanoparticles via electroplating and ultraviolet reduction methods so as
to achieve this purpose. Microstructures, distribution, quantities and spectral
peaks of GO and Ag loading on the Ti sheets surface were characterized.
GO-Ag-Ti multiphase nanocomposite exhibited excellent antimicrobial ability and
anti-adherence performance. Subsequently, morphology, membrane integrity,
apoptosis and relative genes expression of bacteria incubated on the Ti samples
surface were monitored to reveal the bactericidal mechanism. Additionally, the
cytotoxicity of Ti substrates incorporating GO thin film and Ag nanoparticles
were investigated. GO-Ag-Ti composite configuration that have outstanding
antibacterial properties will provide the foundation to study bone integration
in vitro and in vivo in the future.
Keywords: GO-Ag-Ti multiphase nanocomposite,
microstructure and quantities, antibacterial activity, bactericidal mechanism,
cytotoxicity