110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

WWC3 下调与人胃癌不良预后和对胃癌中 Hippo 信号传导的抑制相关
Authors Hou J, Zhou J
Received 15 October 2016
Accepted for publication 10 February 2017
Published 12 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2931—2942
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S124790
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Abstract: The aim of this study was to investigate the clinicopathological
significance and biological roles of WWC3 in human gastric cancer (GC).
Clinical significance of WWC3 in human GCs was examined by using
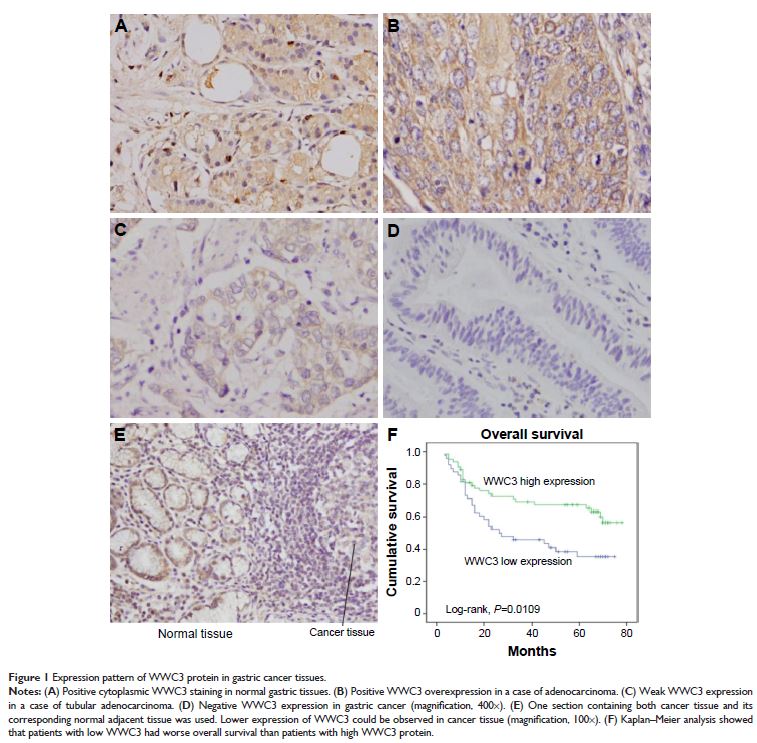
immunohistochemistry (IHC). WWC3 was downregulated in 48 of 111 human GCs, and
its downregulation was associated with advanced stage, positive nodal status,
and higher relapse rate. Importantly, WWC3 downregulation correlated with poor
survival. It was also found that WWC3 protein expression was downregulated in
GC cell lines compared with normal cell line GES-1. On one hand, WWC3
overexpression inhibited the cell growth rate and invading ability in HGC-27
cell line. On the other hand, depleting WWC3 by small interfering RNA (siRNA)
promoted proliferation rate and invading ability in the SGC-7901 cell line. In
addition, cell cycle analysis showed that WWC3 overexpression inhibited while
its depletion accelerated cell cycle progression at the G1/S transition.
Western blot (WB) analysis demonstrated that WWC3 repressed cyclin D1 and cyclin
E while upregulated p27 expression. Luciferase reporter assay showed that WWC3
activated Hippo signaling pathway by suppressing TEAD transcription activity,
with downregulation of total and nuclear YAP and its target CTGF. WWC3 siRNA
depletion exhibited the opposite effects. In conclusion, this study indicates
that WWC3 serves as a tumor suppressor in GC by activating Hippo signaling.
Keywords: WWC3, gastric cancer, cell cycle,
Hippo, YAP