110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

高葡萄糖水平通过 GTP 酶促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖
Authors Hou Y, Zhou M, Xie J, Chao P, Feng Q, Wu J
Received 26 February 2017
Accepted for publication 9 May 2017
Published 13 June 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 429—436
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BCTT.S135665
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Pranela Rameshwar
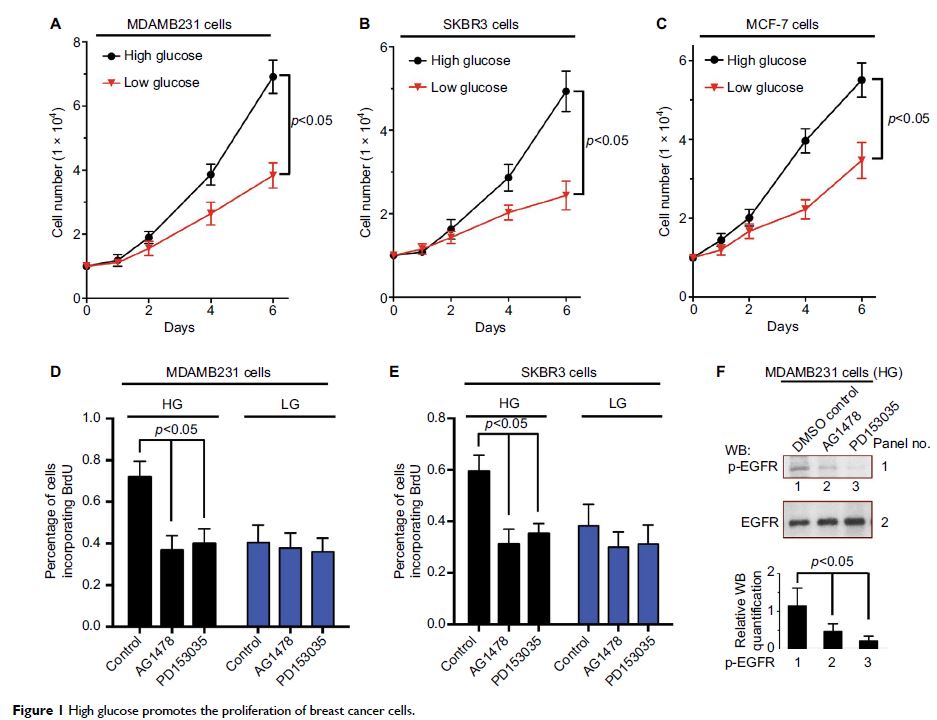
Abstract: Hyperglycemia or diabetes mellitus (DM), which is characterized by high
blood glucose levels, has been linked to an increased risk of cancer for years.
However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the pathophysiological link are
not yet fully understood. In this study, we demonstrate that high glucose
levels promote the proliferation of breast cancer cells by stimulating
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation and the Rho family GTPase
Rac1 and Cdc42 mediate the corresponding signaling induced by high glucose
levels. We further show that Cdc42 promotes EGFR phosphorylation by blocking
EGFR degradation, which may be mediated by the Cbl proteins, whereas the
Rac1-mediated EGFR phosphorylation is independent of EGFR degradation. Our
findings elucidate a part of the underlying molecular mechanism of the link
between high glucose levels and tumorigenesis in breast cancer and may provide
new insights on the therapeutic strategy for cancer patients with diabetes or
hyperglycemia.
Keyword: hyperglycemia, breast cancer, GTPases,
Rac1, Cdc42, EGFR