110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氧化锌纳米颗粒诱导的体外和体内动脉粥样硬化变化
Authors Yan Z, Wang W, Wu Y, Wang W, Li B, Liang N, Wu W
Received 16 February 2017
Accepted for publication 23 May 2017
Published 13 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4433—4442
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S134897
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Yang Liu
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Engineered zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are currently being
produced in high tonnage. Exposure to ZnO-NPs presents potential risks to
cardiovascular system. Thus far, the toxicological effects of ZnO-NPs on
cardiovascular system have not been well characterized. In this study, human
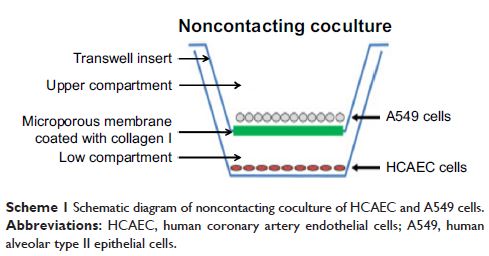
coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) were exposed to ZnO-NPs directly or
indirectly using a transwell coculture system with human alveolar epithelial
cell line A549 to mimic the lung/circulation interaction. It was shown that
levels of proinflammatory mediators (interleukin-8 [IL-8] and tumor necrosis
factor-α [TNF-α]) and biomarkers of atherosclerogenesis (heme oxygenase-1
[HO-1] and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecules-1 [PECAM-1]) in the
supernatants of culture media were significantly increased. Pretreatment of
A549 cells on the apical side of the coculture system with the phagocytosis
inhibitor cytochalasin B (CB) blocked ZnO-NP-induced HO-1 and PECAM-1
expression in HCAEC, indicating that endocytosis of ZnO-NPs by alveolar
epithelial cells was involved in ZnO-NP-induced HO-1 or PECAM-1 expression in
endothelial cells. Moreover, Wistar rats were intratracheally instilled with
ZnO-NP suspension and high fat diet (positive control). ZnO-NP treatment
induced lung and systemic inflammation, dyslipidemia, increased levels of serum
HO-1 and PECAM-1, and aortic pathological damage. Taken together, exposure to
ZnO-NPs could induce atherosclerotic alterations, which might involve
phagocytosis of nanoparticles and inflammation in the lung.
Keywords: zinc oxide nanoparticles,
atherosclerosis, lung inflammation, heme oxygenase-1, platelet endothelial cell
adhesion molecules-1