110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ATIQCTPC: 能够靶向肿瘤并阻断体内血栓形成的纳米医疗
Authors Xu X, Wang Y, Wu J, Hu X, Zhu H, Zhang X, Wang YN, Gui L, Zhao M, Peng S
Received 11 December 2016
Accepted for publication 1 February 2017
Published 13 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4415—4431
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S129989
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: To overcome the harmful side effects, low tolerance, and undesirable
outcomes of the anticancer drugs, we used ethane-1,2-diamine to bridge
antitumoral (S )-3-acetyl-4-oxo-tetrahydroindolo[2,3-a]quinolizine-6-carboxylic
acid (ATIQC) and tumor-targeting d-glucuronic acid, thereby providing (6S )-3-acetyl-4-oxo-N -(2-(3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-carboxamido)ethyl)-4,6,7,12-tetrahydroindolo[2,3-a]quinolizine-6-carboxamide
(ATIQCTPC). Atomic force microscopy images visualized, that in serum, ATIQCTPC
formed particles of height <81 nm. These particles effectively avoided
phagocytosis of macrophages and were stable in blood circulation. Distribution
analysis indicated that ATIQCTPC accumulated and released ATIQC in the tumor
tissue through a targeting manner. Thus, the antitumor and the anti-thrombotic
activities of ATIQCTPC were 100-fold higher than those of ATIQC, and ATIQCTPC
was able to prevent cancer patients from suffering from thrombosis. Based on
the observation that ATIQCTPC decreased serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)
and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in S180 mice, we hypothesized that this is the
mechanism that ATIQCTPC utilized to slow tumor growth. Additionally, we
observed that ATIQCTPC inhibited thrombosis by decreasing serum P-selectin of
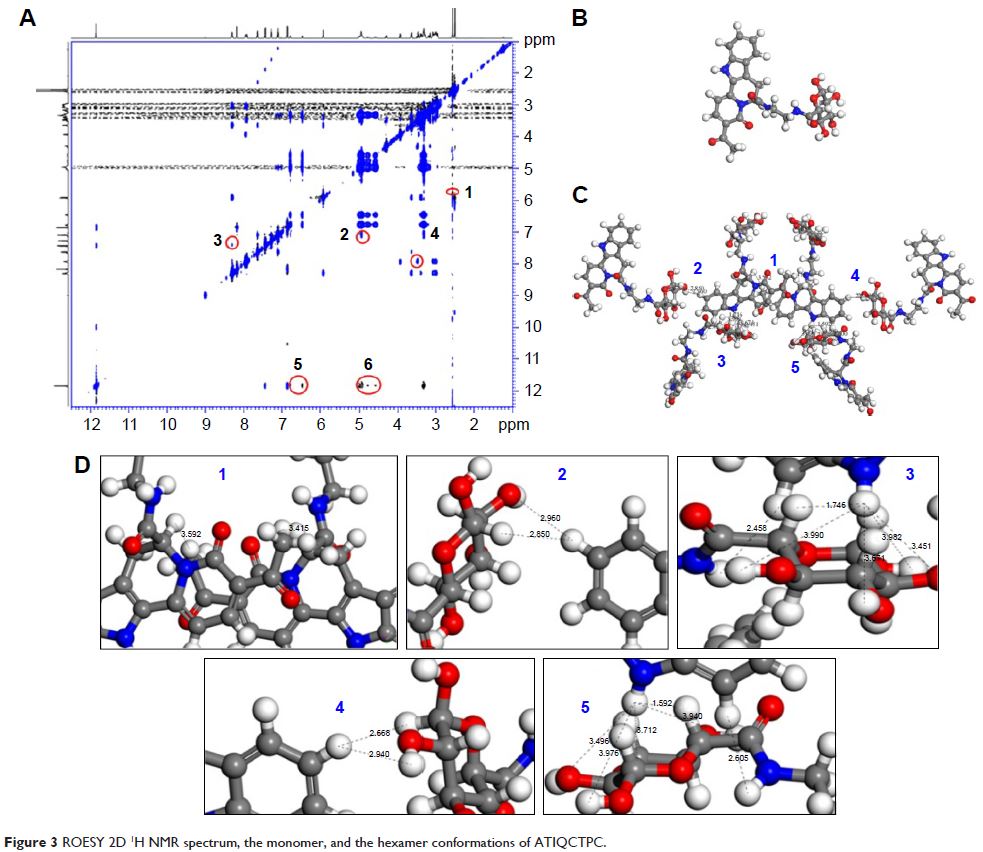
thrombotic rats. The intermolecular association and the hexamerization manner
of ATIQCTPC were experimentally evidenced and correlated with the formation of
the nanoparticles.
Keywords: tumor, thrombosis, targeting,
nanoparticle, TNF-α, IL-8, P-selectin