110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

隐丹参醌 (Cryptotanshinone) 通过胆管癌细胞中的 JAK2/STAT3 和 PI3K /Akt/NFĸB 通路诱导细胞周期停滞和细胞凋亡
Authors Ke FY, Wang Z, Song XL, Ma Q, Hu YP, Jiang L, Zhang YJ, Liu YB, Zhang Y, Gong W
Received 16 January 2017
Accepted for publication 11 May 2017
Published 15 June 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1753—1766
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S132488
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Rajendra Narayan Mitra
Peer reviewer comments 6
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is the most common biliary tract malignancy in
the world with high resistance to current chemotherapies and extremely poor
prognosis. The main objective of this study was to investigate the inhibitory
effects of cryptotanshinone (CTS), a natural compound isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge ,
on CCA both in vitro and in vivo and to explore the underlying mechanisms of
CTS-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
Methods: The anti-tumor activity of CTS on HCCC-9810 and RBE
cells was assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium
bromide (MTT) assay and colony forming assays. Cell cycle changes were detected
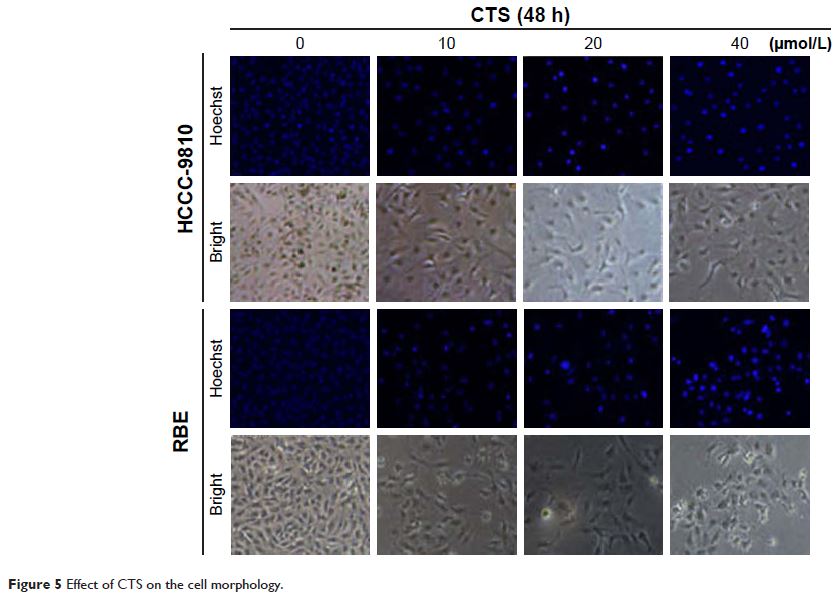
by flow cytometric analysis. Apoptosis was detected by annexin V/propidium
iodide double staining and Hoechst 33342 staining assays. The efficacy of CTS
in vivo was evaluated using a HCCC-9810 xenograft model in athymic nude
mice. The expression of key proteins involved in cell apoptosis and signaling
pathway in vitro was analyzed by Western blot analysis.
Results: CTS induced potent growth inhibition, S-phase arrest,
apoptosis, and colony-forming inhibition in HCCC-9810 and RBE cells in a
dose-dependent manner. Intraperitoneal injection of CTS (0, 10, or 25 mg/kg)
for 4 weeks significantly inhibited the growth of HCCC-9810 xenografts in
athymic nude mice. CTS treatment induced S-phase arrest with a decrease of
cyclin A1 and an increase of cyclin D1 protein level. Bcl-2 expression was
downregulated remarkably, while Bax expression was increased after apoptosis
occurred. Additionally, the activation of JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt/NFκB was
significantly inhibited in CTS-treated CCA cells.
Conclusion: CTS induced CCA cell apoptosis by suppressing both the
JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt/NFκB signaling pathways and altering the expression of
Bcl-2/Bax family, which was regulated by these two signaling pathways. CTS may
serve as a potential therapeutic agent for CCA.
Keywords: cholangiocarcinoma, cryptotanshinone,
apoptosis, JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/Akt/NFκB