110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

改良后的 LFIAs 用于对护理点 BNP 的高敏感检测
Authors Gong Y, Hu J, Choi JR, You M, Zheng Y, Xu B, Wen T, Xu F
Received 27 February 2017
Accepted for publication 5 May 2017
Published 15 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4455—4466
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S135735
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Heart failure (HF) has become a major cause of morbidity and mortality
with a significant global economic burden. Although well-established clinical
tests could provide early diagnosis, access to these tests is limited in
developing countries, where a relatively higher incidence of HF is present.
This has prompted an urgent need for developing a cost-effective, rapid and
robust diagnostic tool for point-of-care (POC) detection of HF. Lateral flow
immunoassay (LFIA) has found widespread applications in POC diagnostics.
However, the low sensitivity of LFIA limits its ability to detect important HF
biomarkers (e.g., brain natriuretic peptide [BNP]) that are normally present in
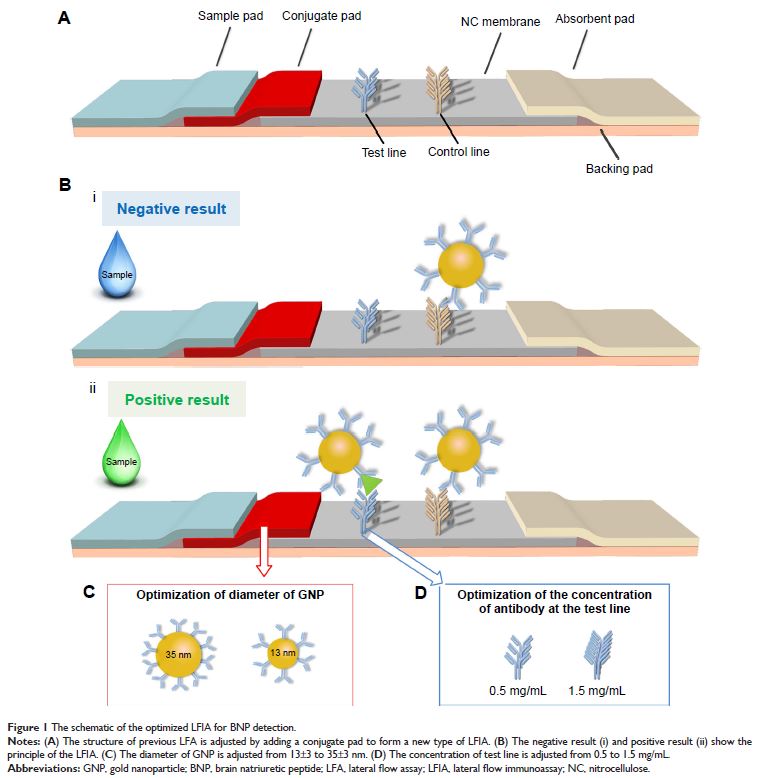
low concentration in blood. To address this issue, we developed an improved
LFIA by optimizing the gold nanoparticle (GNP)–antibody conjugate conditions
(e.g., the conjugate pH and the amount of added antibody), the diameter of GNP
and the concentration of antibody embedded on the test line and modifying the
structure of test strip. Through these improvements, the proposed test strip
enabled the detection of BNP down to 0.1 ng/mL within 10–15 min,
presenting ~15-fold sensitivity enhancement over conventional lateral flow
assay. We also successfully applied our LFIA in the analysis of BNP in human
serum samples, highlighting its potential use for clinical assessment of HF.
The developed LFIA for BNP could rapidly rule out HF with the naked eye,
offering tremendous potential for POC test and personalized medicine.
Keywords: heart failure, biomarker, colorimetric
assays, personalized medicine