110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于生物信息学方法确定与去分化型脂肪肉瘤相关的关键基因和分子机制
Authors Yu H, Pei D, Chen L, Zhou X, Zhu H
Received 13 January 2017
Accepted for publication 20 April 2017
Published 16 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3017—3027
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S132071
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chiung-Kuei Huang
Background: Dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS) is one of the most deadly types of
soft tissue sarcoma. To date, there have been few studies dedicated to
elucidating the molecular mechanisms behind the disease; therefore, the
molecular mechanisms behind this malignancy remain largely unknown.
Materials and methods: Microarray profiles of 46 DDLPS samples and nine
normal fat controls were extracted from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Quality
control for these microarray profiles was performed before analysis.
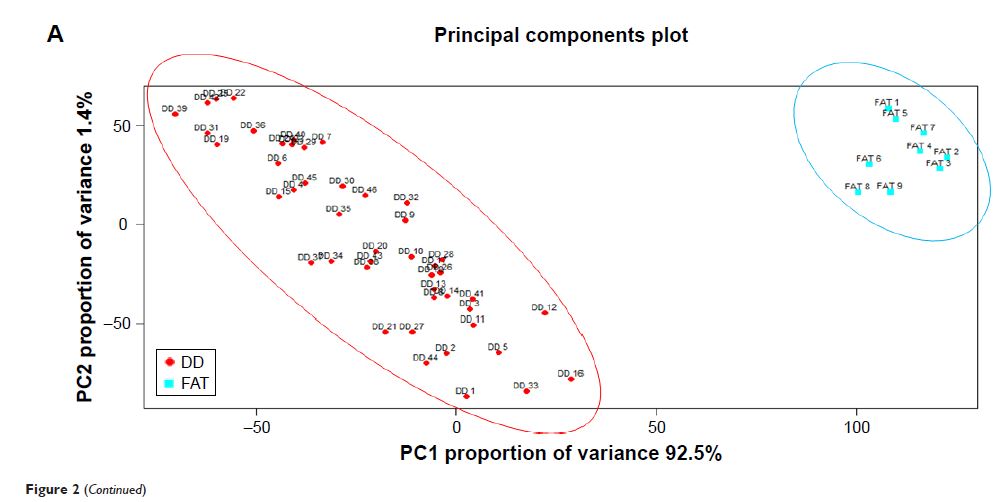
Hierarchical clustering and principal component analysis were used to
distinguish the general differences in gene expression between DDLPS samples
and the normal fat controls. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were
identified using the Limma package in R. Next, the enriched Gene Ontology (GO)
terms and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways were obtained
using the online tool DAVID (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/). A protein–protein
interaction (PPI) network was constructed using the STRING database and
Cytoscape software. Furthermore, the hub genes within the PPI network were
identified.
Results: All 55 microarray profiles were confirmed to be of
high quality. The gene expression pattern of DDLPS samples was significantly
different from that of normal fat controls. In total, 700 DEGs were identified,
and 83 enriched GO terms and three KEGG pathways were obtained. Specifically,
within the DEGs of DDLPS samples, several pathways were identified as being
significantly enriched, including the PPAR signaling pathway, cell cycle
pathway, and pyruvate metabolism pathway. Furthermore, the dysregulated PPI
network of DDLPS was constructed, and 14 hub genes were identified.
Characteristic of DDLPS, the genes CDK4 and MDM2 were universally found to be
up-regulated and amplified in gene copy number.
Conclusion: This study used bioinformatics to comprehensively mine
DDLPS microarray data in order to obtain a deeper understanding of the
molecular mechanism of DDLPS.
Keywords: dedifferentiated liposarcoma,
molecular mechanisms, microarray, bioinformatic methods