110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

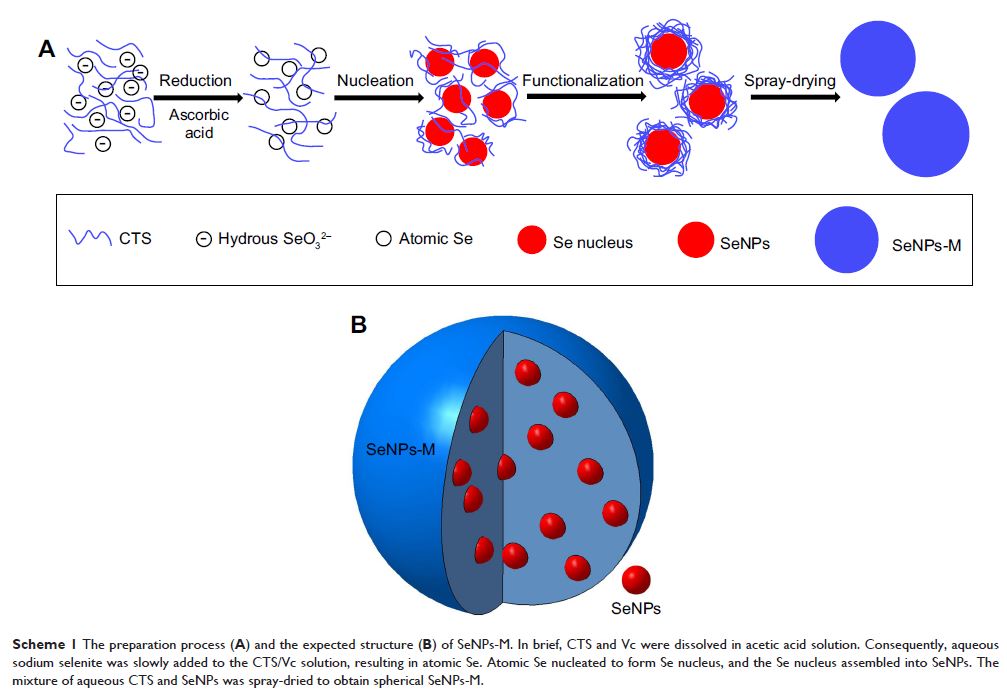
负载壳聚糖微球的硒纳米颗粒的制备及其抗氧化性能
Authors Bai K, Hong B, He J, Hong Z, Tan R
Received 11 December 2016
Accepted for publication 11 February 2017
Published 21 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4527—4539
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S129958
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs), as a special form of selenium (Se)
supplement, have attracted worldwide attention due to their favorable
properties and unique bioactivities. Herein, an eco-friendly and economic way
to prepare stable SeNPs is introduced. SeNPs were synthesized in aqueous
chitosan (CTS) and then embedded into CTS microspheres by spray-drying, forming
selenium nanoparticles-loaded chitosan microspheres (SeNPs-M). The
physicochemical properties including morphology, elemental state, size
distribution and surface potential were investigated. Institute of Cancer
Research mice were used as model animal to evaluate the bioactivities of
SeNPs-M. Trigonal-phase SeNPs of ~35 nm were synthesized, and SeNPs-M
physically embedding those SeNPs were successfully prepared. Amazingly, acute
toxicity test indicated that SeNPs-M were much safer than selenite in terms of
Se dose, with a LD50 of around 18-fold of that of selenite.
In addition, SeNPs-M possessed powerful antioxidant activities, as evidenced by
a dramatic increase of both Se retention and the levels of glutathione
peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and catalase. The design of SeNPs-M can offer
a new way for further development of SeNPs with a higher efficacy and better
biosafety. Thus, SeNPs-M may be a potential candidate for further evaluation as
an Se supplement with antioxidant properties and be used against Se deficiency
in animals and human beings.
Keywords: selenium, nano, microsphere, chitosan,
antioxidant