110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

衍生的嗜中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比率,及单核细胞与淋巴细胞的比率可能成为预测晚期胃癌患者总生存期的更好的生物标志物
Authors Song S, Li C, Li S, Gao H, Lan X, Xue Y
Received 26 March 2017
Accepted for publication 6 May 2017
Published 26 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3145—3154
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S138039
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background and
objectives: Preoperative systemic
inflammatory response and nutritional status play important roles in the
tumorigenesis, progression, and prognosis of gastric cancer (GC). This research
is designed to investigate the prognostic value of the biomarkers including the
neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (dNLR),
monocyte to lymphocyte ratio (MLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and
prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in predicting overall survival in patients
with GC.
Methods: A total of 1,990 consecutive GC patients who underwent
gastrectomy from 2007 to 2011 were enrolled and divided into high level and low
level based on the optimal cut-off points for NLR, dNLR, MLR, PLR, and PNI,
respectively. The clinicopathological characteristics of the two levels were
comparatively analyzed. Overall survival analysis was executed using these
biomarkers and clinicopathological characteristics.
Results: The number of metastatic lymph nodes, distant
metastasis, American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM stage, radicality, tumor
size, metastatic lymph nodes ratio, ascites, and Hb were all significantly
associated with NLR, dNLR, MLR, PLR, and PNI. All of these five biomarkers were
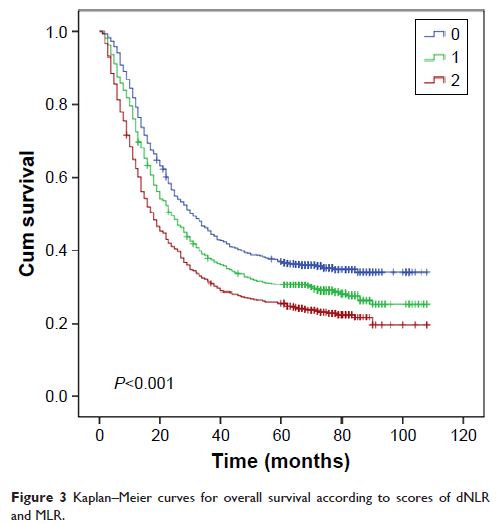
closely associated with overall survival in univariate analyses, but only dNLR
and MLR were significant in multivariate model. dNLR and MLR can be bonded to
predict survival, but whether separate or together, dNLR and MLR were mainly
significant in advanced stages.
Conclusion: Although preoperative NLR, dNLR, MLR, PLR, and PNI in
peripheral blood proved significant prediction of prognoses of postoperative GC
patients, dNLR and MLR may be better biomarkers for predicting overall
survival, especially in advanced GC patients.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, prognosis, survival, biomarker, systemic inflammatory response