110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

将吉非替尼 (Gefitinib) 用于一线和二线治疗时,对晚期表皮生长因子受体外显子 19 或 21 突变阳性肺癌患者的疗效比较
Authors Patel N, Wu P, Zhang H
Received 2 April 2017
Accepted for publication 6 June 2017
Published 28 June 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 243—248
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S138643
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Alexandra Fernandes
Objectives: Gefitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeting epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR), shows excellent clinical benefit in treating advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The aim of this study was to compare the
efficacy and toxicity of gefitinib as first-line therapy and second-line
therapy for advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients with positive exon 21 (L858R)
or exon 19 deletion of EGFR mutation.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the
clinical data of 60 EGFR -mutated advanced lung
adenocarcinoma patients from July 2011 to November 2015 who have received oral
gefitinib 250 mg once daily. Gefitinib was taken until disease
progression, intolerable toxicity or death.
Results: After a median follow-up of
792 days, one death had occurred. Among the 59 patients who survived, 17
patients progressed. Overall, the median progression-free survival (mPFS) was
10 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 7.53–12.46 months, p <0.05). The
response rate (RR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 33.33% and 71.66%,
respectively. However, there was longer mPFS in the first line-therapy than
that in the second-line therapy: in the first-line gefitinib therapy, mPFS was
12 months among 41 patients (95% CI: 9.58–14.41 months, p <0.05), and in
the second-line therapy, mPFS was 7 months among 19 patients (95% CI:
1.31–12.68 months, p <0.05). Furthermore, in
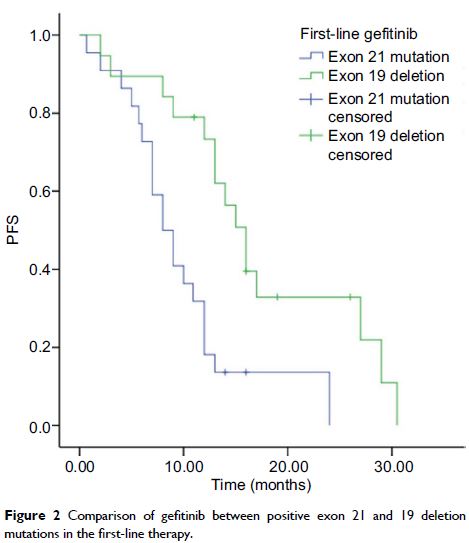
subgroup analyses examining different EGFR mutation types, we noted that mPFS was
significantly longer for patients with exon 19 deletion than for those with
positive exon 21 in both the first-line therapy and second-line therapy.
Conclusion: Patients with advance lung adenocarcinoma who were
selected by positive exon 21 or 19 deletion mutations had significantly longer
mPFS in the first-line therapy than that in the second-line therapy when
treated with gefitinib. EGFR mutation types may influence the
response to gefitinib therapy.
Keywords: gefitinib, epidermal growth factor
receptor, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, lung adenocarcinoma