110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

一种新型局部麻醉系统:以转录反式激活剂肽装饰的纳米载体用于皮下递送罗哌卡因 (Ropivacaine)
Authors Chen CY, You PJ
Received 1 March 2017
Accepted for publication 8 April 2017
Published 28 June 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1941—1949
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S135916
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Purpose: Barrier properties of the skin and physicochemical properties of drugs
are the main factors for the delivery of local anesthetic molecules. The
present work evaluates the anesthetic efficacy of drug-loaded nanocarrier (NC)
systems for the delivery of local anesthetic drug, ropivacaine (RVC).
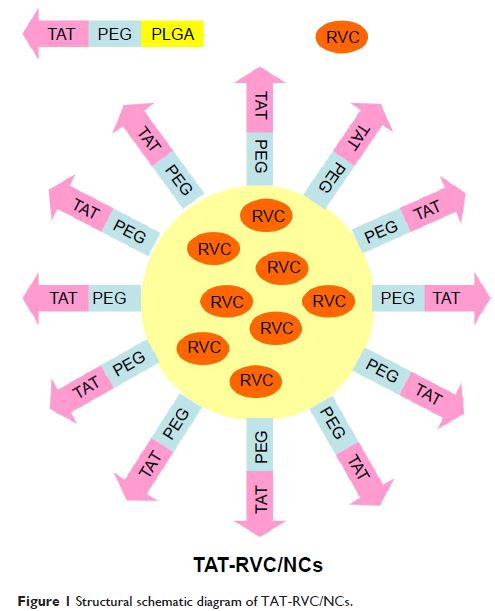
Methods: In this study, transcriptional transactivator peptide (TAT)-decorated RVC-loaded
NCs (TAT-RVC/NCs) were successfully fabricated. Physicochemical properties of
NCs were determined in terms of particle size, zeta potential, drug
encapsulation efficiency, drug-loading capacity, stability, and in vitro drug
release. The skin permeation of NCs was examined using a Franz diffusion cell
mounted with depilated mouse skin in vitro, and in vivo anesthetic effect was
evaluated in mice.
Results: The results showed that TAT-RVC/NCs have a mean diameter of
133.2 nm and high drug-loading capacity of 81.7%. From the in vitro skin
permeation results, it was observed that transdermal flux of TAT-RVC/NCs was
higher than that of RVC-loaded NCs (RVC/NCs) and RVC injection. The evaluation
of in vivo anesthetic effect illustrated that TAT-RVC/NCs can enhance the
transdermal delivery of RVC by reducing the pain threshold in mice.
Conclusion: These results indicate that TAT-decorated NCs systems are useful for
overcoming the barrier function of the skin, decreasing the dosage of RVC and
enhancing the anesthetic effect. Therefore, TAT-decorated NCs can be used as an
effective transdermal delivery system for local anesthesia.
Keywords: local anesthetic system, ropivacaine, transcriptional transactivator
peptide, nanocarriers, skin delivery