110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

循环 miR-223 对不同癌症监测的影响:一项综合分析
Authors Zhang YF, Lin JB, Huang WJ, Cao Y, Liu Y, Wang TQ, Zhong WY, Wang DL, Mao RR, Chen XL
Received 24 March 2017
Accepted for publication 12 May 2017
Published 28 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3193—3201
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S137837
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ru Chen
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Purpose: Abnormal expression of miR-223 in cancerous tissue has confirmed it as
an important player in tumorigenesis of cancers, such as hepatocellular
carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, osteosarcoma, gastric cancer, and chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. The present meta-analysis aimed to explore the
association between circulating miR-223 and prognosis of cancers.
Methods: The studies were accessed by an electronic search of multiple databases.
RevMan5.3 and STATA14.0 were used to estimate the heterogeneity among studies,
pooled effects, and publication bias.
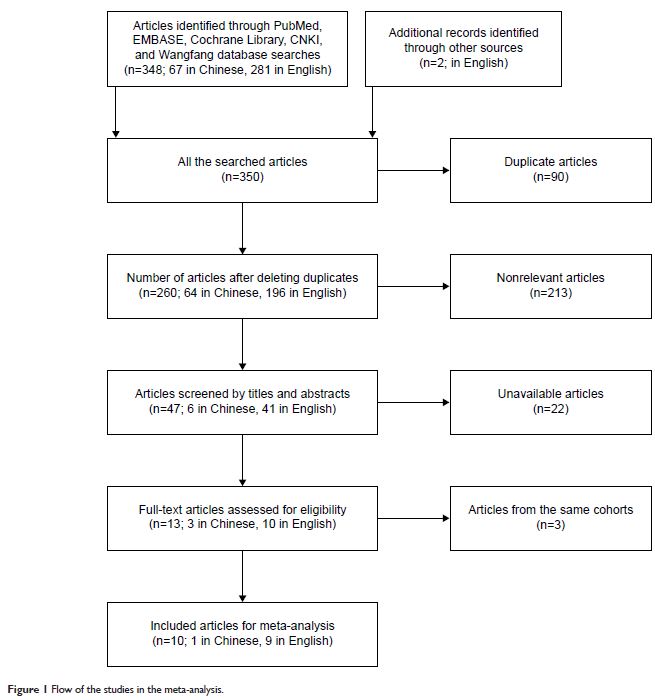
Results: Ten studies with data of 1,002 patients with cancer were included in
this meta-analysis. The risk of metastasis from stages 3 to 4 of TNM did not
decrease when high versus low circulating expression of miR-223 were compared
(pooled odds ratio =0.50, 95% CI: 0.24–1.03). In case of prognosis, the overall
survival time was not significantly longer with high circulating miR-223
expression (pooled hazard ratio [HR] =0.64, 95% CI: 0.38–1.11) in all cancer
types. However, the overall survival time of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
(pooled HR =0.19, 95% CI: 0.07–0.54) increased in subgroup analysis. Moreover,
the treatment-free survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia was significantly
increased with high circulating miR-223 expression (pooled HR =0.38, 95% CI:
0.23–0.64).
Conclusion: Circulating miR-223 was not an effective biomarker in prognosis
surveillance in all cancers but in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Keywords: miR-223, carcinoma, metastasis, prognosis, meta-analysis