110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雌激素受体 αPvuII 和 XbaI 多态性与前列腺癌易感性和危险分层的关系:基于病例对照研究的综合分析
Authors Zhao YN, Zheng X, Zhang LJ, Hu Q, Guo YT, Jiang H, Shi SN, Zhang X
Received 14 January 2017
Accepted for publication 29 March 2017
Published 29 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3203—3210
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S132419
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: Studies on the
association between two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in estrogen
receptor α (ERα), PvuII (rs2234693 T>C) and XbaI (rs9340799 A>G), and the
prostate cancer risk are inconsistent. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis
to derive a more accurate estimation of this relationship.
Methods: A literature search of PubMed, Embase, Web of
Science databases until October 1, 2016, was conducted. Crude odds ratios
(ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to assess the
strength of this association.
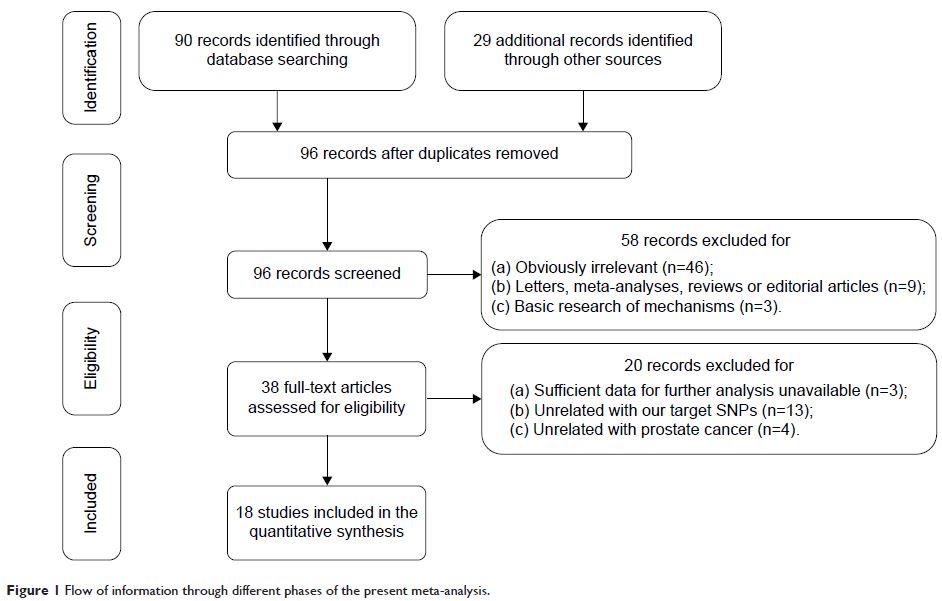
Results: Eighteen case-control studies, with a total of
3,317 prostate cancer patients and 8,324 controls, were included. Results
showed that both PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms were significantly associated
with a higher prostate cancer risk in overall populations. To derive a more
accurate estimation, subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity revealed that
this relationship existed only in Caucasians, but not in Asians. Furthermore,
PvuII polymorphism was significantly associated with high Gleason grade
(Gleason score ≥7) cancers.
Conclusion: The current meta-analysis demonstrates that ERα
PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms are associated with a higher prostate cancer risk
in Caucasians, but not in Asians, and PvuII polymorphism is significantly
associated with high Gleason grade tumors, indicating the probability of
inherited susceptibility to prostate cancer arising from different genomic ERα
SNPs, which may help us understand the pathogenesis of prostate cancer in
Caucasians.
Keywords: estrogen
receptor α, PvuII, XbaI, prostate cancer, meta-analysis