110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LincRNA-p21 通过 miR-9/E-钙粘附蛋白级联信号通路分子机制抑制肝细胞癌的侵袭和转移
Authors Ding G, Peng Z, Shang J, Kang Y, Ning HB, Mao CS
Received 16 February 2017
Accepted for publication 4 April 2017
Published 30 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3241—3247
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S134910
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Abstract: In the
previous study, it was found that long intergenic noncoding RNA-p21
(lincRNA-p21) was downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and
lincRNA-p21 overexpression inhibited tumor invasion through inducing
epithelial–mesenchymal transition. However, the underlying mechanism was not
fully elaborated. In this study, lincRNA-p21 expression was measured in 12
paired HCC and nontumor adjacent normal tissues by quantitative real-time
polymerase chain reaction. The effects of lincRNA-p21 on HCC cells were studied
using lentivirus expressing lincRNA-p21 vector in vitro. The association
between lincRNA-p21 level and miR-9 level was tested with the Spearman rank
correlation. The effects of miR-9 on HCC cells were studied by using miR-9
inhibitor in vitro. Luciferase assay was used to validate the target of miR-9.
The results showed that lincRNA-p21 was downregulated in human HCC tissues and
cell lines. LincRNA-p21 overexpression significantly inhibited HCC cell
migration and invasion in vitro. Besides, lincRNA-p21 negatively regulated
miR-9 expression level, and miR-9 was upregulated in human HCC tissues and
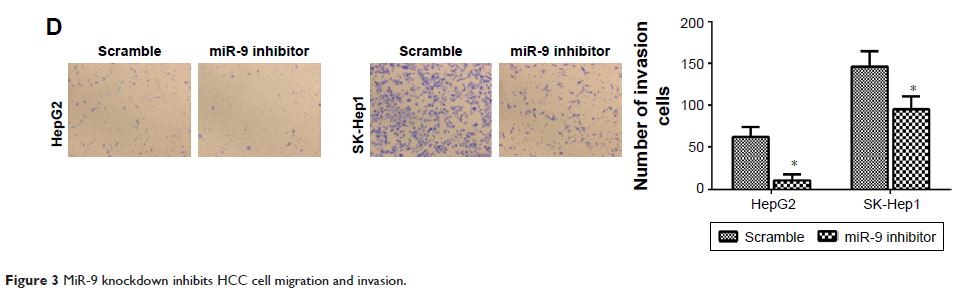
cells. MiR-9 knockdown inhibited HCC cell migration and invasion in vitro. Finally,
the luciferase assay results showed that E-cadherin was a direct target of
miR-9. The expression level of E-cadherin was found to be regulated by
lincRNA-p21 and miR-9. Altogether, the results suggested that lincRNA-p21
inhibits migration and invasion of HCC cells through regulating miR-9-mediated
E-cadherin cascade signaling pathway.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, lincRNA-p21, miR-9, E-cadherin,
epithelial–mesenchymal transition