110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

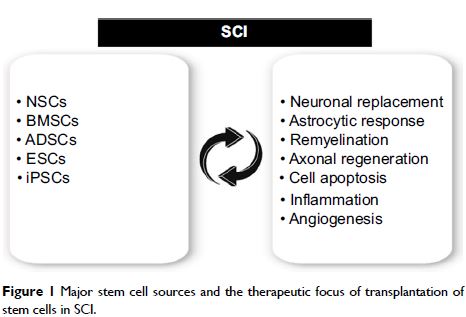
干细胞为主的疗法治疗脊髓损伤:一个回顾分析
Authors Shi Z, Huang H, Feng S
Received 14 April 2017
Accepted for publication 14 June 2017
Published 3 July 2017 Volume 2017:5 Pages 125—131
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JN.S139677
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Hari Shanker Sharma
Abstract: Spinal
cord injury (SCI) is a devastating condition and major burden on society and
individuals. Currently, neurorestorative strategies, including stem cell
therapy products or mature/functionally differentiated cell-derived cell
therapy products, can restore patients with chronic complete SCI to some degree
of neurological functions. The stem cells for neurorestoration include neural
stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent
stem cells, etc. A better understanding of the merits, demerits and precise
function of different stem cells in the treatment of SCI may aid in the
development of neurorestorative strategies. However, the efficacy, safety and
ethical concerns of stem cell-based therapy continue to be challenged.
Nonetheless, stem cell-based therapies hold promise of widespread applications,
particularly in areas of SCI, and have the potential to be novel therapeutics,
which contributes to the repair of SCI. This review mainly focused on recent
advances regarding the stem cell-based therapies in the treatment of SCI and
discussed future perspectives in this field.
Keywords: spinal cord injury, neural stem cells, bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells, adipose-derived stem cells, embryonic stem cells,
induced pluripotent stem cells