110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

多肽 N -乙酰氨基半乳糖转移酶-6 在胃癌中的表达
Authors Guo Y, Shi JJ, Zhang J, Li HX, Liu B, Guo H
Received 1 April 2017
Accepted for publication 14 June 2017
Published 7 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3337—3344
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S138590
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Abstract: Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related
deaths, with limited improvement in its clinical outcome worldwide. Aberrant
mucin-type O -glycosylation is a critical
event widespread in the development of GC. Polypeptide N -acetylgalactosaminyltransferases
(GALNTs) regulate the initial step and determine the sites of mucin-type O -glycoprotein biosynthesis.
GALNT6 has considerable potential as a biomarker in various cancers. The roles
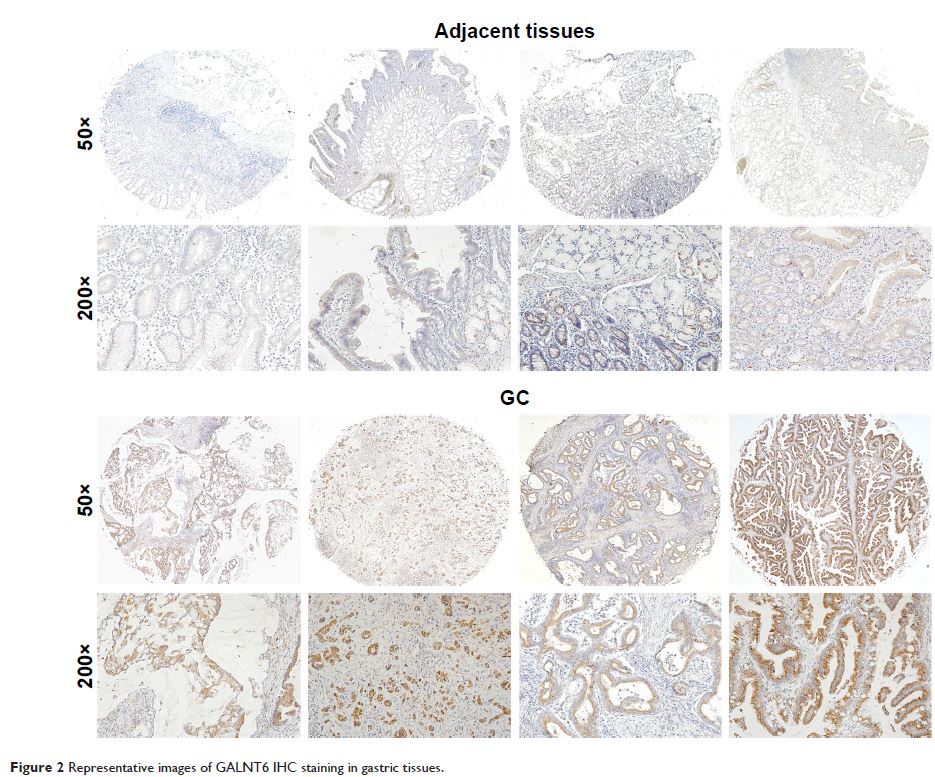
of GALNT6 in GC were analyzed, and the results showed that GALNT6 expression
markedly increased in GC tissues compared with those in adjacent gastric
tissues. High intratumoral GALNT6 density was associated with the
clinicopathological parameters of TNM stage and distant metastasis. GALNT6 was
identified as an independent prognosticator for the poor prognosis of GC
patients. Moreover, the high expression level of GALNT6 was significantly
associated with the low expression levels of E-cadherin and β-catenin and the
high expression levels of MMP9. These findings indicated that GALNT6 could
provide new insights into the characterization of GC as well as contribute to
the development of an efficient prognostic indicator and novel therapeutic
modalities for GC.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, O -glycosylation, GALNT6, prognosis