110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用装载多柔比星 (Doxorubicin) 的单唾液酸神经节苷脂胶束系统在神经脑胶质瘤中跨越血脑屏障,增进抗肿瘤活性及进行神经修复
Authors Zou D, Wang W, Lei D, Yin Y, Ren P, Chen J, Yin T, Wang B, Wang G, Wang Y
Received 29 March 2017
Accepted for publication 7 June 2017
Published 7 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4879—4889
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S138257
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: For the treatment of glioma and other central nervous system
diseases, one of the biggest challenges is that most therapeutic drugs cannot
be delivered to the brain tumor tissue due to the blood–brain barrier (BBB).
The goal of this study was to construct a nanodelivery vehicle system with
capabilities to overcome the BBB for central nervous system administration.
Doxorubicin as a model drug encapsulated in ganglioside GM1 micelles was able
to achieve up to 9.33% loading efficiency and 97.05% encapsulation efficiency
by orthogonal experimental design. The in vitro study demonstrated a slow and
sustainable drug release in physiological conditions. In the cellular uptake
studies, mixed micelles could effectively transport into both human umbilical
vein endothelial cells and C6 cells. Furthermore, biodistribution imaging of
mice showed that the DiR/GM1 mixed micelles were accumulated sustainably and
distributed centrally in the brain. Experiments on zebrafish confirmed that
drug-loaded GM1 micelles can overcome the BBB and enter the brain. Among all
the treatment groups, the median survival time of C6-bearing rats after
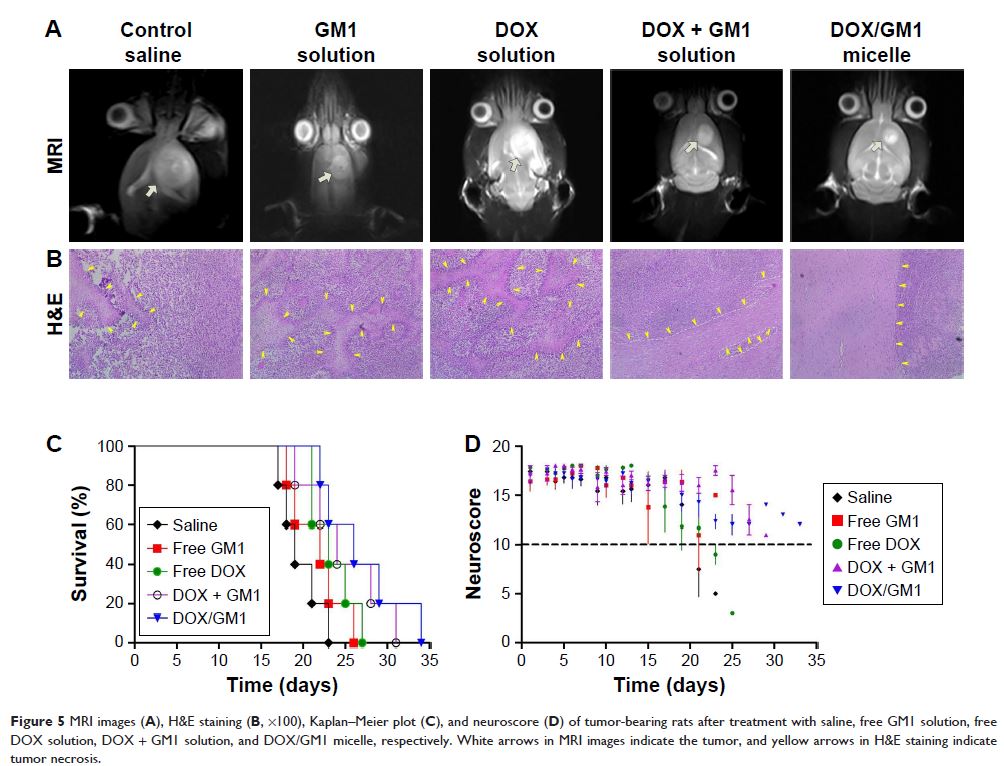
administering DOX/GM1 micelles was significantly prolonged. In conclusion, the
ganglioside nanomicelles developed in this work can not only penetrate BBB
effectively but also repair nerves and kill tumor cells at the same time.
Keywords: blood–brain
barrier, GM1, nanovesicles, doxorubicin, glioma, zebrafish