110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

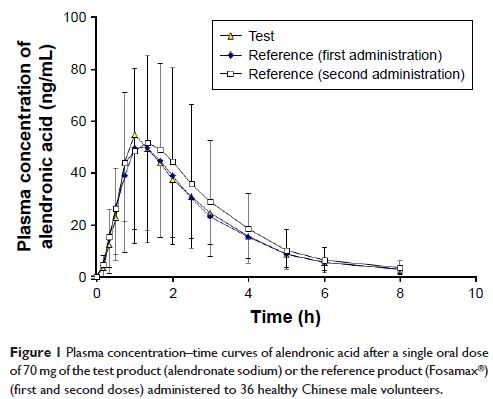
在空腹健康志愿者中通用阿仑膦酸钠 (Alendronate sodium) 片剂 (70mg) 与 Fosamax® 片剂 (70mg) 的生物等效性对比:一项随机、开放标签、三向、重复引用交叉研究
Authors Zhang Y, Chen X, Tang Y, Lu Y, Guo L, Zhong D
Received 29 March 2017
Accepted for publication 22 May 2017
Published 11 July 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2109—2119
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S138286
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristian Vilos
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the bioequivalence of a
generic product 70 mg alendronate sodium tablets with the reference product
Fosamax® 70 mg tablet.
Materials and methods: A
single-center, open-label, randomized, three-period, three-sequence,
reference-replicated crossover study was performed in 36 healthy Chinese male
volunteers under fasting conditions. In each study period, the volunteers
received a single oral dose of the generic or reference product (70 mg).
Blood samples were collected at pre-dose and up to 8 h after
administration. The bioequivalence of the generic product to the reference
product was assessed using the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and
European Medicines Agency (EMA) reference-scaled average bioequivalence (RSABE)
methods.
Results: The average maximum concentrations (C max) of alendronic
acid were 64.78±43.76, 56.62±31.95, and 60.15±37.12 ng/mL after the single dose
of the generic product and the first and second doses of the reference product,
respectively. The areas under the plasma concentration–time curves from time 0
to the last timepoint (AUC0–t )
were 150.36±82.90, 148.15±85.97, and 167.11±110.87 h·ng/mL, respectively.
Reference scaling was used because the within-subject standard deviations of
the reference product (sWR ) for C max and AUC0–t were all higher than the cutoff value of 0.294.
The 95% upper confidence bounds were -0.16 and -0.17 for C max and AUC0–t , respectively, and the point estimates for the
generic/reference product ratio were 1.08 and 1.00, which satisfied the RSABE
acceptance criteria of the FDA. The 90% CIs for C max and AUC0–t were 90.35%–129.04% and 85.31%–117.15%,
respectively, which were within the limits of the EMA for the bioequivalence of
69.84%–143.19% and 80.00%–125.00%.
Conclusion: The generic product was bioequivalent to the
reference product in terms of the rate and extent of alendronate absorption
after a single 70 mg oral dose under fasting conditions.
Keywords: alendronate
sodium, pharmacokinetics, highly variable drug, reference-scaled average
bioequivalence