110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

直接金属激光烧结植入物对糖尿病小猪的骨结合早期的影响
Authors Tan NW, Liu XW, Cai YH, Zhang SJ, Jian B, Zhou YC, Xu XR, Ren S, Wei HB, Song YL
Received 1 April 2017
Accepted for publication 2 June 2017
Published 31 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5433—5442
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S138615
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: High failure rates of oral implants have been reported in diabetic
patients due to the disruption of osseointegration. The aim of this study was
to investigate whether direct laser metal sintering (DLMS) could improve
osseointegration in diabetic animal models.
Methods: Surface characterizations were carried out on
two types of implants. Cell morphology and the osteogenic-related gene
expression of MG63 cells were observed under conditions of DLMS and microarc
oxidation (MAO). A diabetes model in mini-pigs was established by intravenous
injection of streptozotocin (150 mg/kg), and a total of 36 implants were
inserted into the mandibular region. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and
histologic evaluations were performed 3 and 6 months after implantation.
Results: The Ra (the average of the absolute height of
all points) of MAO surface was 2.3±0.3 µm while the DLMS surface showed the Ra
of 27.4±1.1 µm. The cells on DLMS implants spread out more podia than those on
MAO implants through cell morphology analysis. Osteogenic-related gene
expression was also dramatically increased in the DLMS group. Obvious
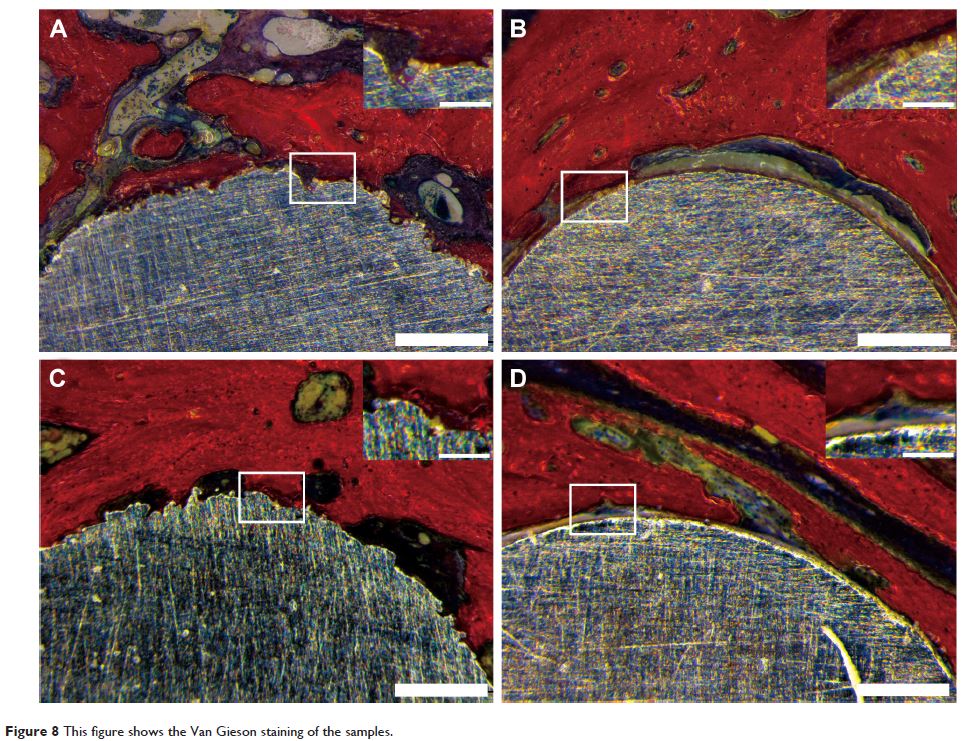
improvement was observed in the micro-CT and Van Gieson staining analyses of
DLMS implants compared with MAO at 3 months, although this difference
disappeared by 6 months. DLMS implants showed a higher bone–implant contact
percentage (33.2%±11.2%) at 3 months compared with MAO group (18.9%±7.3%) while
similar results were showed at 6 months between DLMS group (42.8%±10.1%) and
MAO group (38.3%±10.8%).
Conclusion: The three-dimensional environment of implant
surfaces with highly porous and fully interconnected channel and pore
architectures can improve cell spreading and accelerate the progress of
osseointegration in diabetic mini-pigs.
Keywords: laser
manufacturing, dental implants, diabetes mellitus, osseointegration