110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

新抗癌药物的细胞内运输: 抗体 - 药物偶联物
Authors Kalim M, Chen J, Wang S, Lin C, Ullah S, Liang K, Ding Q, Chen S, Zhan JB
Received 24 February 2017
Accepted for publication 31 May 2017
Published 2 August 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2265—2276
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S135571
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
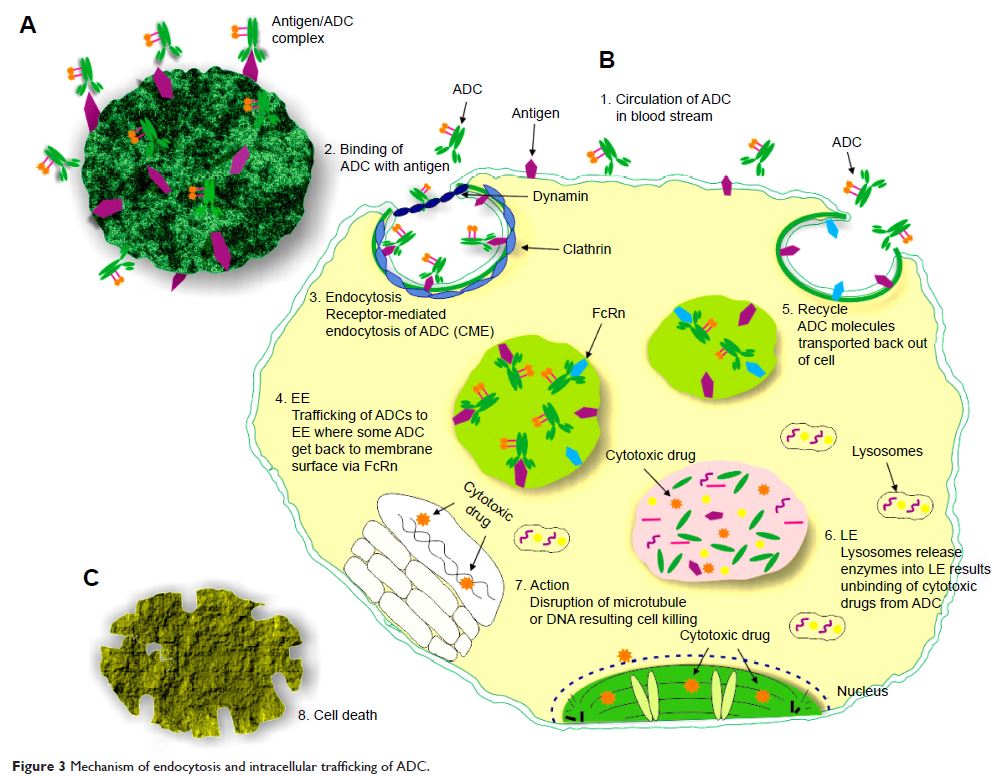
Abstract: Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC)
is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal
antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes
place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and
pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking
optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for
researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of
endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum
recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is
significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular
trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and
biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer
treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking
of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate
practically applicable ADCs.
Keywords: antibody–drug
conjugate, antibody, endocytosis, intracellular trafficking, clathrin