110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

岩藻糖基转移酶 VII (Fucosyltransferase VII) 通过 EGFR/AKT/mTOR 通路促进 A549 细胞中的增殖
Authors Liang J, Gao W, Cai L
Received 2 May 2017
Accepted for publication 26 June 2017
Published 7 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3971—3978
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S140940
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
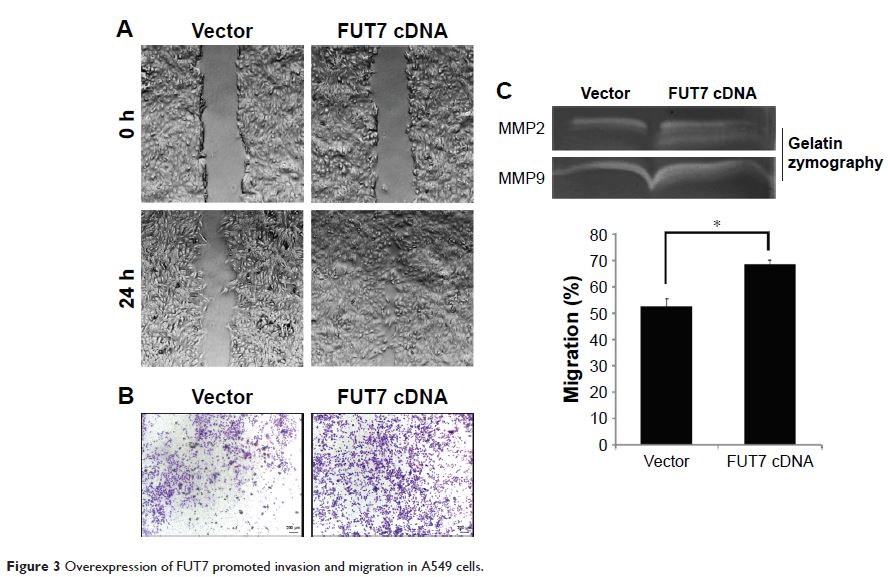
Abstract: Fucosyltransferase VII (FUT7) is one of a1,3-fucosyltransferases family
that catalyzes the final fucosylation step in the synthesis of Lewis antigens
and generates a unique glycosylated product sialyl Lewis X (sLeX). sLeX can serve
as ligands for E- or P-selectin expressed on the cell surface and results in
cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. However, the molecular biological
mechanisms of FUT7 elevation in neoplastic cells are still largely unknown. In
this study, we examined the impact of FUT7 on cell proliferation and migration
in A549 cells by colony formation assay, cell cycle assay, gelatin zymography,
wound-healing assay, transwell invasion assay and Western blot. In addition, we
identified that FUT7 activated EGFR/AKT/mTOR signal pathway that correlated
with sLeX augmentation. In conclusion, FUT7 overexpression
augments sLeX synthesis to trigger cell proliferation via
the activation of EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, which indicated that FUT7
may be a potential therapeutic target for epithelial cancers with a high
expression of FUT7 and sLeX.
Keywords: fucosyltransferase
VII, epidermal growth factor receptor, lung cancer, proliferation, signal
pathway