110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

电针刺和普瑞巴林 (Pregabalin) 对眼镜蛇毒诱导的大鼠三叉神经痛模型的认知作用
Authors Chen RW, Liu H, An JX, Qian XY, Jiang YD, Cope DK, Williams JP, Zhang R, Sun LN
Received 2 May 2017
Accepted for publication 23 June 2017
Published 8 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1887—1897
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S140840
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr E. Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of
electro-acupuncture (EA) and pregabalin on cognition impairment induced by
chronic trigeminal neuralgia (TN) in rats.
Design: Controlled
animal study.
Setting: Department of Anesthesiology, Pain Medicine and
Critical Care Medicine, Aviation General Hospital of China Medical University.
Subjects: Forty adult male Sprague Dawley rats.
Methods: Rats were randomly divided into four groups. The TN
model was induced by administration of cobra venom to the left infraorbital
nerve. On postoperative day 14, either EA or pregabalin was administered, free
behavioral activities were observed. Spatial learning and memory abilities were
determined in the Morris water maze. The ultrastructural alterations of the
Gasserian ganglion, medulla oblongata and hippocampus were examined by electron
microscopy. The changes on long-term potentiation were investigated.
Results: After treatment, the exploratory behavior
increased and the grooming behavior decreased (P <0.05)
for the EA group and pregabalin group compared with the cobra venom group;
moreover, demyelination of neurons in Gasserian ganglion and medulla oblongata
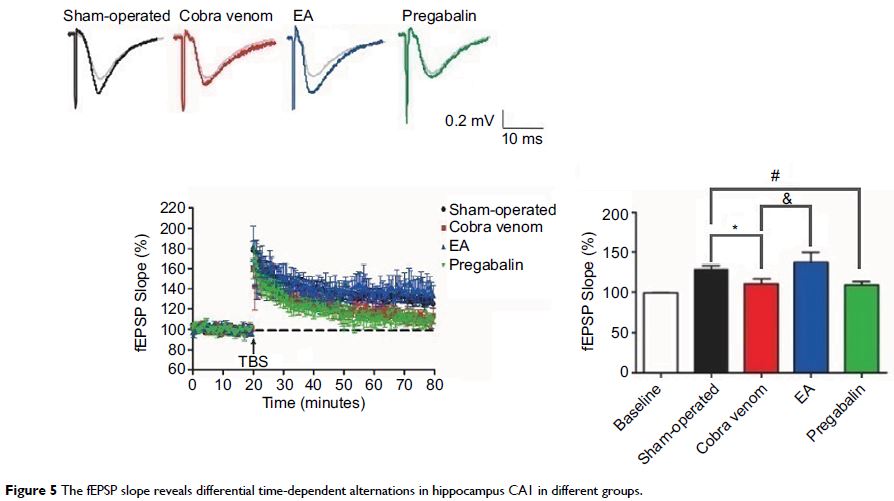
was reversed. The number of platform site crossings, the average percentages of
time in the target quadrant and the field excitatory postsynaptic potential
slopes increased (P <0.05) in the EA group
compared to the cobra venom group. However, the pregabalin group showed no differences
compared to the cobra venom group (P >0.05).
Vacuolar degeneration in the hippocampal neurons was mild in the EA group,
while it was severe in the pregabalin group.
Conclusion: EA and pregabalin could alleviate TN induced by cobra
venom. EA could also inhibit the cognition deficit induced by TN, while
pregabalin could not.
Keywords: TN, cognition
dysfunction, EA, pregabalin, LTP