110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

以叶酸 (Folate) 受体为靶向并封装 2-脱氧葡萄糖和 α 生育酚琥珀酸脂 (α-tocopheryl succintae) 的共同递送纳米载体可增强体内的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Lei X, Li K, Liu Y, Wang ZY, Ruan BJ, Wang L, Xiang A, Wu D, Lu Z
Received 28 February 2017
Accepted for publication 23 May 2017
Published 8 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5701—5715
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S135849
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Bhavesh Kevadiya
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: A combination administration of chemical agents was highlighted to
treat tumors. Recently, tumor cell has been found to be different from normal
cell in metabolic manner. Most of cancer cells prefer aerobic glycolysis to
mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to satisfy energy and biomass
synthesis requirement to survive, grow and proliferate, which provides novel
and potential therapeutic targets for chemotherapy. Here, 2-deoxy-d-glucose
(2-DG), a potent inhibitor of glucose metabolism, was used to inhibit
glycolysis of tumor cells; α-tocopheryl succinate (α-TOS), a water-insoluble
vitamin E derivative, was chosen to suppress OXPHOS. Our data demonstrated that
the combination treatment of 2-DG and α-TOS could significantly promote the
anti-tumor efficiency in vitro compared with administration of the single drug.
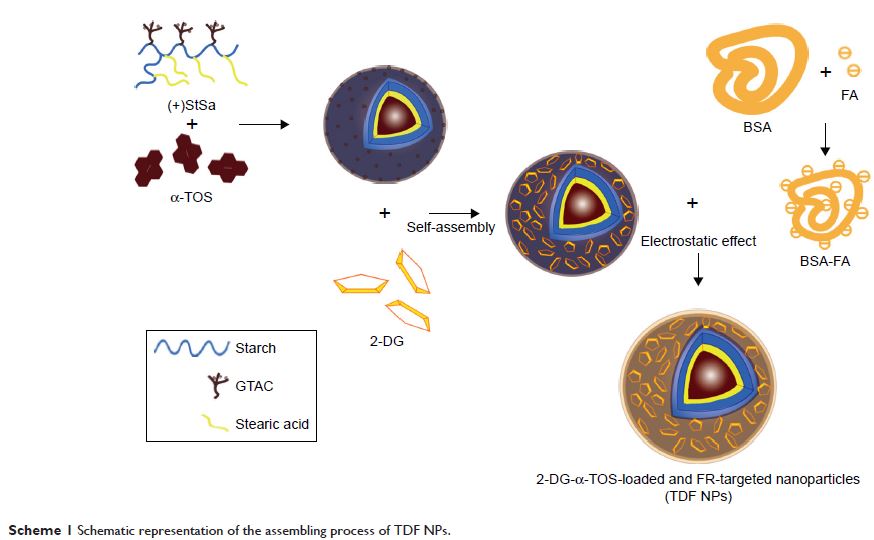
In order to maximize therapeutic activity and minimize negative side effects, a
co-delivery nanocarrier targeting folate receptor (FR) was developed to
encapsulate 2-DG and α-TOS simultaneously based on our previous work.
Transmission electron microscope, dynamic light scattering method and
UV-visible spectrophotometers were used to investigate morphology, size
distribution and loading efficiency of the α-TOS-2-DG-loaded and FR-targeted
nanoparticles (TDF NPs). The TDF NPs were found to possess a layer-by-layer
shape, and the dynamic size was <100 nm. The final encapsulation
efficiencies of α-TOS and 2-DG in TDF NPs were 94.3%±1.3% and 61.7%±7.7% with
respect to drug-loading capacities of 8.9%±0.8% and 13.2%±2.6%, respectively.
Almost no α-TOS release was found within 80 h, and release of 2-DG was
sustained and slow within 72 h. The results of FR binding assay and
fluorescence biodistribution revealed that TDF NPs could target FR highly
expressed on tumor cell in vitro and in vivo. Further, in vivo anti-tumor
experiments showed that TDF NPs had an improved biological function with less
toxicity. Thus, our work indicates that the co-delivery TDF NPs have a great
potential in tumor therapy.
Keywords: co-delivery
nanocarrier, α-tocopheryl succinate, 2-deoxyglucose, anti-tumor