110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

硒纳米粒子的抑制活性结合奥司他韦 (Oseltamivir) 的功效用于治疗 H1N1 流感病毒
Authors Li Y, Lin Z, Guo M, Xia Y, Zhao M, Wang C, Xu T, Chen T, Zhu B
Received 2 May 2017
Accepted for publication 13 July 2017
Published 9 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5733—5743
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S140939
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
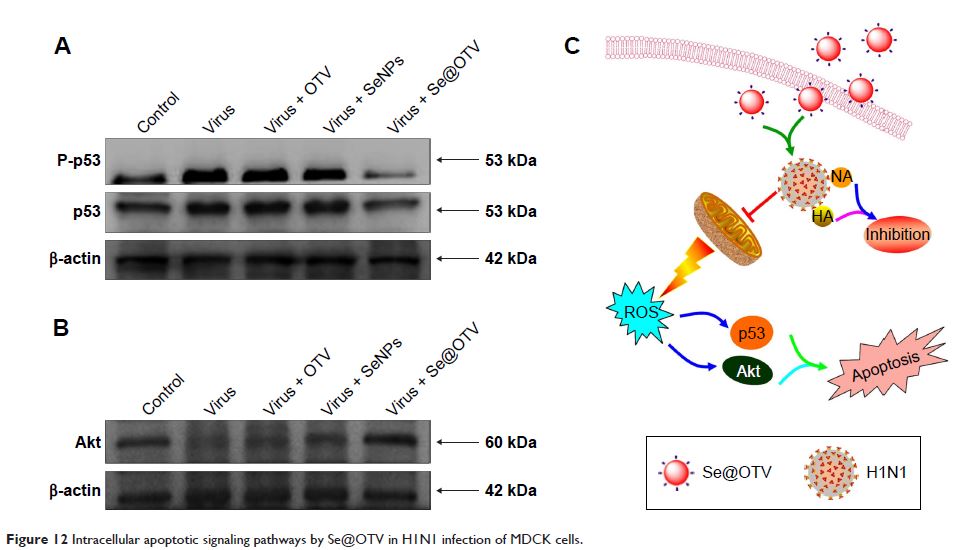
Abstract: As an effective antiviral agent, the clinical application of
oseltamivir (OTV) is limited by the appearance of drug-resistant viruses. Due
to their low toxicity and excellent activity, the antiviral capabilities of
selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) has attracted increasing attention in recent
years. To overcome the limitation of drug resistance, the use of modified NPs
with biologics to explore novel anti-influenza drugs is developing rapidly. In
this study, OTV surface-modified SeNPs with superior antiviral properties and
restriction on drug resistance were synthesized. OTV decoration of SeNPs
(Se@OTV) obviously inhibited H1N1 infection and had less toxicity. Se@OTV interfered
with the H1N1 influenza virus to host cells through inhibiting the activity of
hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. The mechanism was that Se@OTV was able to
prevent H1N1 from infecting MDCK cells and block chromatin condensation and DNA
fragmentation. Furthermore, Se@OTV inhibited the generation of reactive oxygen
species and activation of p53 phosphorylation and Akt. These results
demonstrate that Se@OTV is a promising efficient antiviral pharmaceutical for
H1N1.
Keywords: selenium
nanoparticles, oseltamivir, influenza virus, neuraminidase, apoptosis