110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

尼莫单抗 (Nimotuzumab) 结合放化疗对中国局部晚期宫颈癌患者的安全性和有效性
Authors Chen Y, Tang W, Pan X, Wu C, Cao Y, Yang W
Received 2 February 2017
Accepted for publication 27 April 2017
Published 17 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4113—4119
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S133756
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Objective: To evaluate efficacy and safety of nimotuzumab combined with
chemotherapy and radiotherapy in women with locally advanced cervical cancer.
Materials and methods: Women with locally advanced cervical cancer (stage
IIB, III, or IVA) who experienced relapse after first-line chemoradiotherapy
and one or more lines of palliative chemotherapy were enrolled. All patients
received nimotuzumab weekly at 200 mg/m2 as single
agent for 4 weeks (induction phase), then concurrent with 6 cycles (21-day per
cycle) of gemcitabine (800 mg/m2) or cisplatin
(50 mg/m2) for 18 weeks (concurrent phase) and then once
every 2 weeks (maintenance phase). Overall response rate (ORR) was assessed
after 4 weeks of induction therapy and then every 3 months according to
response evaluation criteria in solid tumors version 1.1 (primary end point).
Secondary end points include progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival
(OS), and drug toxicity. Descriptive statistics was used for ORR, and Kaplan–Meier
curves were generated for OS and PFS.
Results: A total of 80 women with locally advanced cervical
cancer were enrolled and evaluated for safety and efficacy. Our results
demonstrated that none of the patients had a complete response (0%), 11 patients
had a partial response (14%), and 10 patients had progressive disease (13%),
giving a tumor response rate of 14%. A total of 59 patients had stable disease
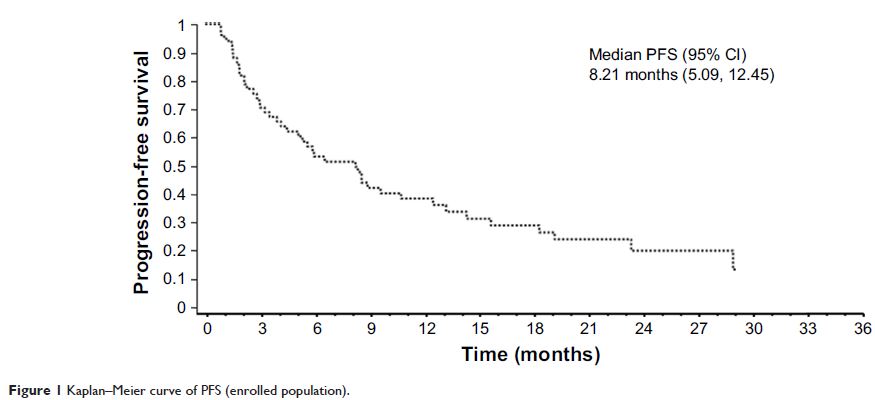
(74%), giving a disease control rate of 88% (70/80). Median PFS was 8.21 months
(95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.09–12.45). Median OS was 11.96 months (95% CI:
8.11–23.95). The most common adverse events were mucositis, myelosuppression,
and gastrointestinal disturbance.
Conclusion: Our study results suggested that nimotuzumab in
combination with chemotherapy and radiotherapy is well tolerated, and could be
a better treatment alternative in patients with locally advanced cervical
cancer.
Keywords: nimotuzumab,
metastatic cervical cancer, Chinese patients, radiotherapy, chemoradiotherapy