110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

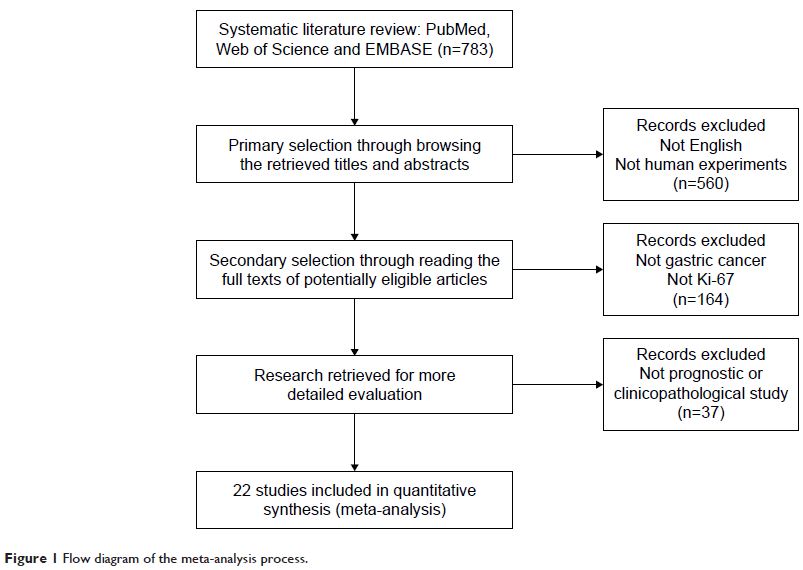
Ki-67 免疫组化表达在胃癌中的临床病理和预后意义:一个系统综述和荟萃分析
Authors Liu G, Xiong DS, Zeng JJ, Chen BR, Huang ZJ
Received 3 June 2017
Accepted for publication 1 August 2017
Published 1 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4321—4328
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143089
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Abstract: The prognostic significance
of Ki-67 in patients with gastric cancer (GC) remains controversial. The aim of
our meta-analysis is to evaluate its association with clinicopathological
characteristics and prognostic value in patients with GC. PubMed, EMBASE, and
Web of Science were systematically searched up to May 2017. Twenty-two studies
including 3,825 patients with GC were analyzed. The meta-analysis indicated
that the incidence difference of Ki-67 expression in GC patients was
significant when comparing the older group to younger group (odds ratio [OR]
=1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.19, 1.75), lymph node positive group to
negative group (OR =1.49, 95% CI 1.20, 1.84), the large size tumor group to the
small size tumor group (OR =1.27, 95% CI 1.24, 1.68) and the TNM stage III+IV
group to TNM stage I+II group (OR =2.28, 95% CI 1.66, 3.12). However, no
statistical differences existed in gender. The detection of Ki-67 significantly
correlated with the overall survival of patients (hazard ratio =1.51, 95% CI
1.31, 1.72). Our study suggested that Ki-67 overexpression was associated with
poor prognosis in GC patients. Ki-67 positive rates may be associated with age,
lymph node metastasis, tumor size, and TNM staging system in GC patients.
Keywords: Ki-67, gastric
cancer, meta-analysis, prognostic