110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

人参皂苷 (Ginsenoside) Rg1 纳米颗粒穿透血脑屏障,改善糖尿病脑梗死大鼠的大脑机能
Authors Shen J, Zhao Z, Shang W, Liu C, Zhang B, Zhao L, Cai H
Received 13 April 2017
Accepted for publication 2 August 2017
Published 5 September 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6477—6486
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S139602
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Dongwoo Khang
Abstract: Diabetic cerebral infarction
is with poorer prognosis and high rates of mortality. Ginsenoside Rg1 (Rg1) has
a wide variety of therapeutic values for central nervous system (CNS) diseases
for the neuron protective effects. However, the blood–brain barrier (BBB)
restricts Rg1 in reaching the CNS. In this study, we investigated the
therapeutic effects of Rg1 nanoparticle (PHRO, fabricated with γ-PGA, L-PAE
(H), Rg1, and OX26 antibody), targeting transferrin receptor, on the diabetes
rats complicated with diabetic cerebral infarction in vitro and in vivo.
Dynamic light scattering analysis shows the average particle size of PHRO was
79±18 nm and the polydispersity index =0.18. The transmission electron
microscope images showed that all NPs were spherical in shape with diameters of
89±23 nm. PHRO released Rg1 with sustained release manner and could promote the
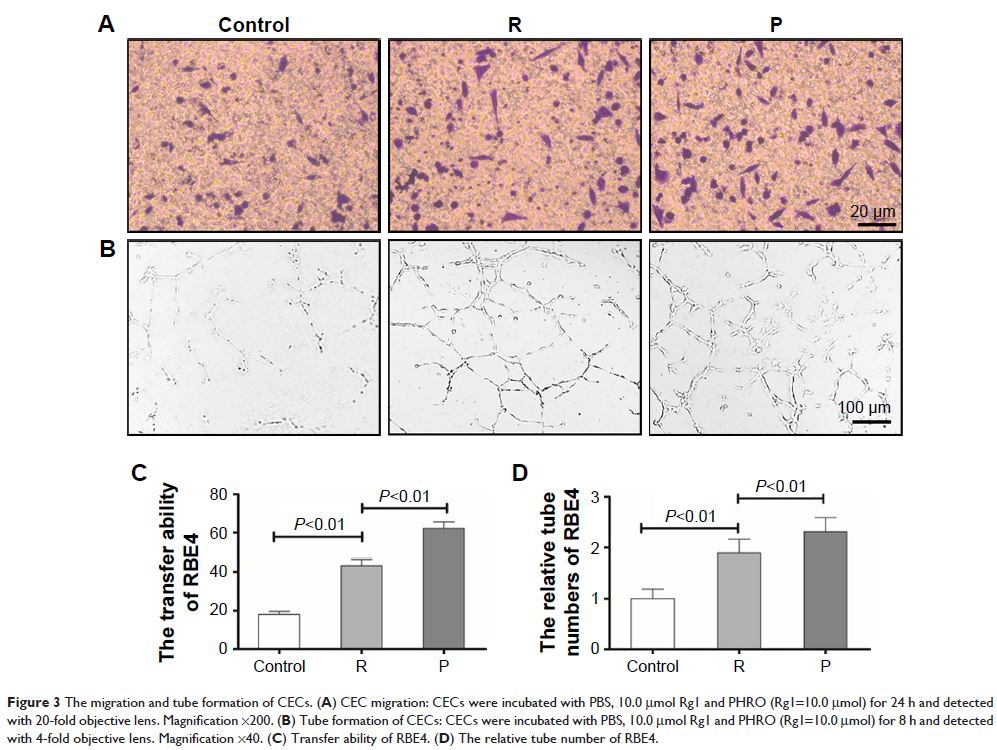
migration of cerebrovascular endothelial cells and tube formation and even
penetrated the BBB in vitro. PHRO could penetrate the BBB with high
concentration in brain tissue to reduce the cerebral infarction volume and
promote neuronal recovery in vivo. PHRO was promising to be a clinical
treatment of diabetes mellitus with cerebral infarction.
Keywords: poly-γ-glutamic
acid, ginsenoside Rg1, OX26, blood–brain barrier