110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CXCR4 拮抗剂 AMD3100 引发镇痛效果,同时恢复 GlyRα3 表达以减轻神经性疼痛
Authors Liu X, Liu H, Dai L, Ma BJ, Ma K
Received 13 April 2017
Accepted for publication 10 July 2017
Published 7 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2205—2212
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S139619
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr E. Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Objective: Chemokine
CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 have been reported to play a critical role in
neurogenesis and neuronal differentiation. Recently, some reports have implicated
this chemokine signaling in the pathogenesis of many kinds of pain. However,
its role in neuropathic pain (NP) is still largely unclear. This study explored
the distribution and function of CXCR4 in spinal cord (SC) dorsal horn (DH) in
a rat L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model.
Methods: Rats received repeated intrathecal injection of CXCR4 antagonist
AMD3100. Behavioral assessments were conducted using a traditional “up–down”
method. The spinal CXCL12 contents were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent
assay. The expression and distribution of CXCR4 in the SC were determined by
immunoflurescence and Western blot. GlyRα3 expressions were also measured by
Western blot or immunofluorescence.
Results: SNL induced CXCL12–CXCR4 activation in the spinal DH. Intrathecal
administration of AMD3100 alleviated the chronic NP against SNL (P <0.01). CXCR4 was colocalized
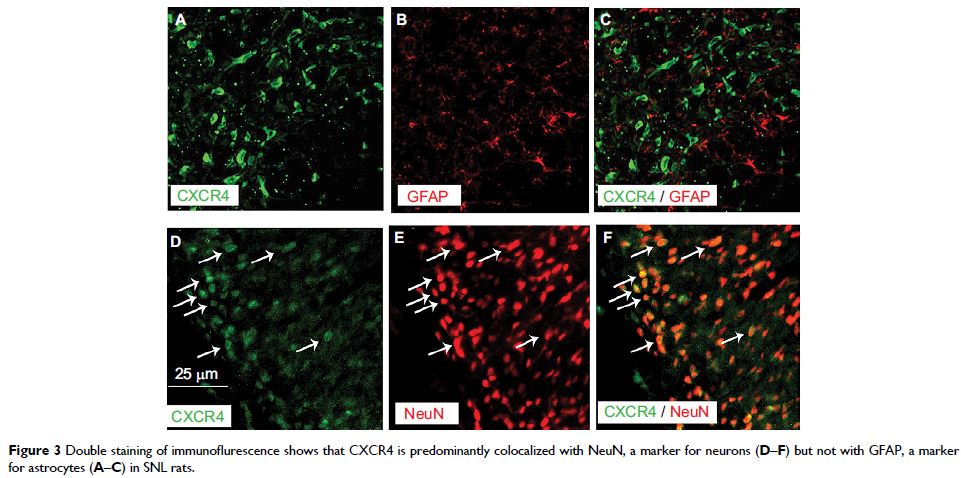
with GlyRα3-positive neurons in the spinal DH at ratio >97%. Meanwhile,
AMD3100 rescued the decrease of GlyRα3 expression (P <0.01
vs the SNL group on Day 14 and Day 21).
Conclusion: CXCR4 antagonist can elicit analgesic effects and restore the
inhibitory neurotransmission such as GlyRα3 against NP.
Keywords: neuropathic pain, CXCL12, CXCR4, GlyRα3, L5 spinal nerve ligation