110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过纳米颗粒递送芍药醇 (Paeonol) 可增强体外和体内抗肿瘤作用
Authors Chen C, Jia F, Hou Z, Ruan S, Lu Q
Received 14 June 2017
Accepted for publication 8 August 2017
Published 7 September 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6605—6616
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S143938
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Paeonol (Pae;
2'-hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone) has attracted intense attention as a
potential therapeutic agent against various cancers. However, the use of Pae is
limited owing to its hydrophobicity. Recently, biodegradable polymeric
nanoparticles with amphiphilic copolymers have been used as drug carriers;
these have better bioavailability and are promising tumor-targeted drug
delivery systems. In the current study, we prepared Pae-loaded nanoparticles
(Pae-NPs) with amphiphilic block copolymers using nanoprecipitation. The
physiochemical characteristics and antitumor effects of nanoparticles were
evaluated in different cancer cells.
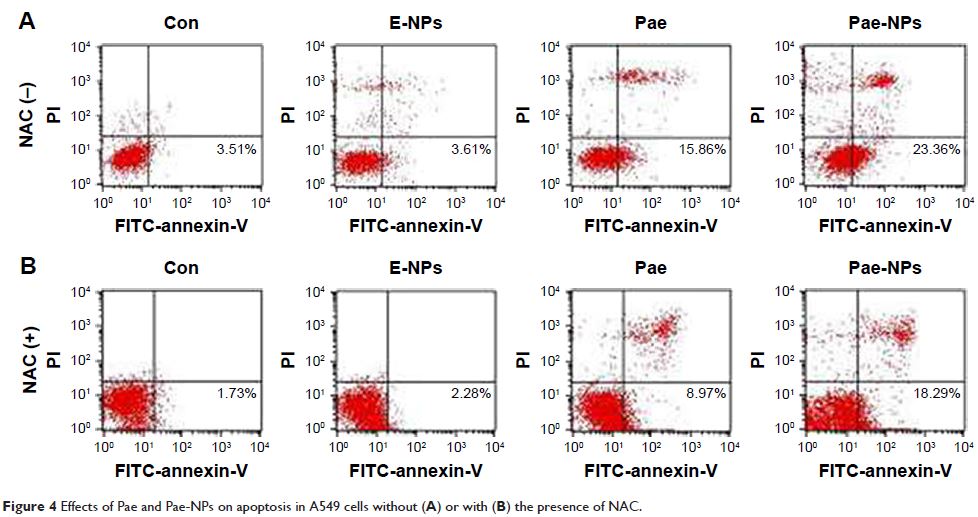
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assays showed
substantial inhibition of cell growth by Pae-NPs. Moreover, lower doses of
Pae-NPs inhibited cell growth more efficiently than the equivalent doses of
free Pae. Inhibition was characterized by significant elevation of
intracellular reactive oxygen species and subsequent inhibition of Akt and
regulation of apoptotic proteins, which could be partly reversed by
pretreatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine. In vivo results also
demonstrated that Pae-NPs could exert much stronger antitumor effects than free
Pae. Therefore, Pae-NPs represent a promising delivery system to overcome the
low solubility of Pae and enable its use in treating cancer.
Keywords: nanoparticles,
drug delivery, paeonol