110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DEPTOR 下调通过 PI3K /Akt/mTOR 通路抑制骨肉瘤的增殖、迁移和存活
Authors Hu B, Lv X, Gao F, Chen S, Wang S, Qing X, Liu J, Wang B, Shao Z
Received 8 June 2017
Accepted for publication 1 August 2017
Published 8 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4379—4391
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143518
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Abstract: Accumulating evidence
reveals that DEP-domain containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR) plays
pivotal roles in the pathogenesis and progression of many tumors. However, the
expression level of DEPTOR and its function in the tumorigenesis of
osteosarcoma (OS) remain unknown. In this study, we conducted quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry to
detect DEPTOR expression level in human OS tissues and cell lines. To assess
DEPTOR function, DEPTOR siRNA was designed and transfected into OS cells, which
were then used in a series of in vitro assays. Our results indicated that
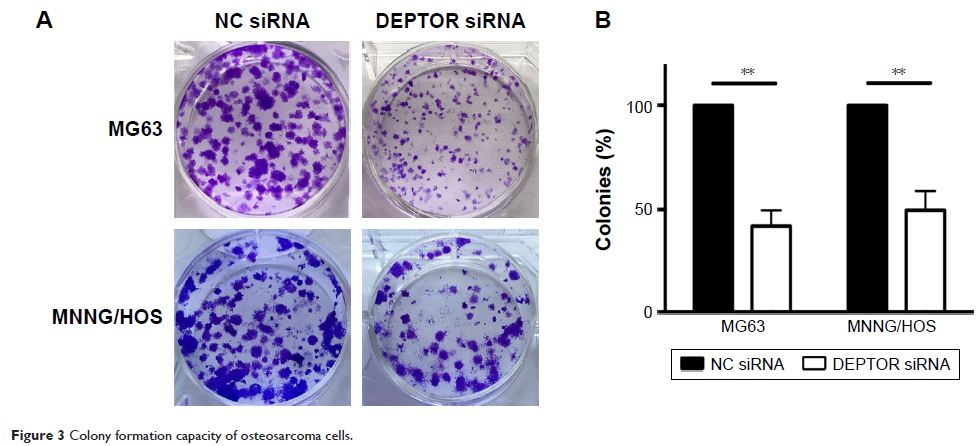
DEPTOR was highly expressed in some OS tissues and cell lines. DEPTOR knockdown
by siRNA dramatically inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and
the formation of vasculogenic mimicry in OS cells. In addition, DEPTOR
knockdown induced cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase and apoptosis in the OS
cell lines, MG63 and MNNG/HOS. Furthermore, we found that DEPTOR knockdown
notably activated mTOR and inhibited the PI3K/Akt pathway. Taken together,
these results suggest that DEPTOR overexpression is necessary for the
proliferation, migration, invasion, formation of vasculogenic mimicry, and
survival of OS cells and may be a potential target for the treatment of OS.
Keywords: osteosarcoma,
DEPTOR, PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, proliferation, apoptosis