110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

含氟非尼酮 (Fluorofenidone) 、由亚精胺 (spermidine) 介导的聚乳酸乙醇酸共聚物纳米粒子,用于治疗特发性肺纤维化
Authors Tang J, Li JM, Li G, Zhang HT, Wang L, Li D, Ding JS
Received 27 April 2017
Accepted for publication 18 July 2017
Published 8 September 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6687—6704
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S140569
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a progressive, fatal lung disease with
poor survival. The advances made in deciphering this disease have led to the
approval of different antifibrotic molecules, such as pirfenidone and
nintedanib. An increasing number of studies with particles (liposomes,
nanoparticles [NPs], microspheres, nanopolymersomes, and nanoliposomes)
modified with different functional groups have demonstrated improvement in
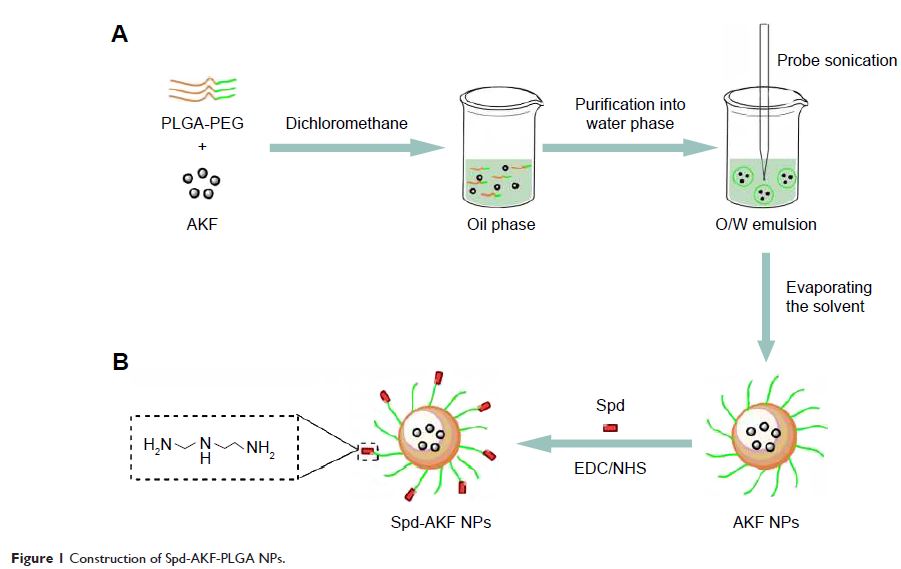
lung-targeted drug delivery. In the present study, we prepared, characterized,
and evaluated spermidine (Spd)-modified poly(lactic-co -glycolic
acid) (PLGA) NPs as carriers for fluorofenidone (AKF) to improve the
antifibrotic efficacy of this drug in the lung. Spd-AKF-PLGA NPs were prepared
and functionalized by modified solvent evaporation with Spd and polyethylene
glycol (PEG)-PLGA groups. The size of Spd-AKF-PLGA NPs was 172.5±4.3 nm. AKF
release from NPs was shown to fit the Higuchi model. A549 cellular uptake of an
Spd–coumarin (Cou)-6-PLGA NP group was found to be almost twice as high as that
of the Cou-6-PLGA NP group. Free Spd and difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) were
preincubated in A549 cells to prove uptake of Spd-Cou-6-PLGA NPs via a
polyamine-transport system. As a result, the uptake of Spd-Cou-6-PLGA NPs
significantly decreased with increased Spd concentrations in incubation. At
higher Spd concentrations of 50 and 500 µM, uptake of Spd-Cou-6-PLGA NPs
reduced 0.34- and 0.49-fold from that without Spd pretreatment. After pretreatment
with DFMO for 36 hours, cellular uptake of Spd-Cou-6-PLGA NPs reached 1.26-fold
compared to the untreated DFMO group. In a biodistribution study, the
drug-targeting index of Spd-AKF-PLGA NPs in the lung was 3.62- and 4.66-fold
that of AKF-PLGA NPs and AKF solution, respectively. This suggested that
Spd-AKF-PLGA NPs accumulated effectively in the lung. Lung-histopathology
changes and collagen deposition were observed by H&E staining and Masson
staining in an efficacy study. In the Spd-AKF-PLGA NP group, damage was further
improved compared to the AKF-PLGA NP group and AKF-solution group. The results
indicated that Spd-AKF-PLGA NPs are able to be effective nanocarriers for
anti–pulmonary fibrosis therapy.
Keywords: idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis, fluorofenidone, spermidine, polyamine transport system,
nanoparticles