110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Cationic lipid-based nanoparticles mediate functional delivery of acetate to tumor cells in vivo leading to significant anticancer effects
Authors Brody LP, Sahuri-Arisoylu M, Parkinson JR, Parkes HG, So PW, Hajji N, Thomas EL, Frost GS, Miller AD, Bell JD
Received 2 March 2017
Accepted for publication 29 April 2017
Published 8 September 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6677—6685
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S135968
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas J Webster
Abstract: Metabolic reengineering using nanoparticle delivery represents an
innovative therapeutic approach to normalizing the deregulation of cellular
metabolism underlying many diseases, including cancer. Here, we demonstrated a
unique and novel application to the treatment of malignancy using a short-chain
fatty acid (SCFA)-encapsulated lipid-based delivery system –
liposome-encapsulated acetate nanoparticles for cancer applications (LITA-CAN).
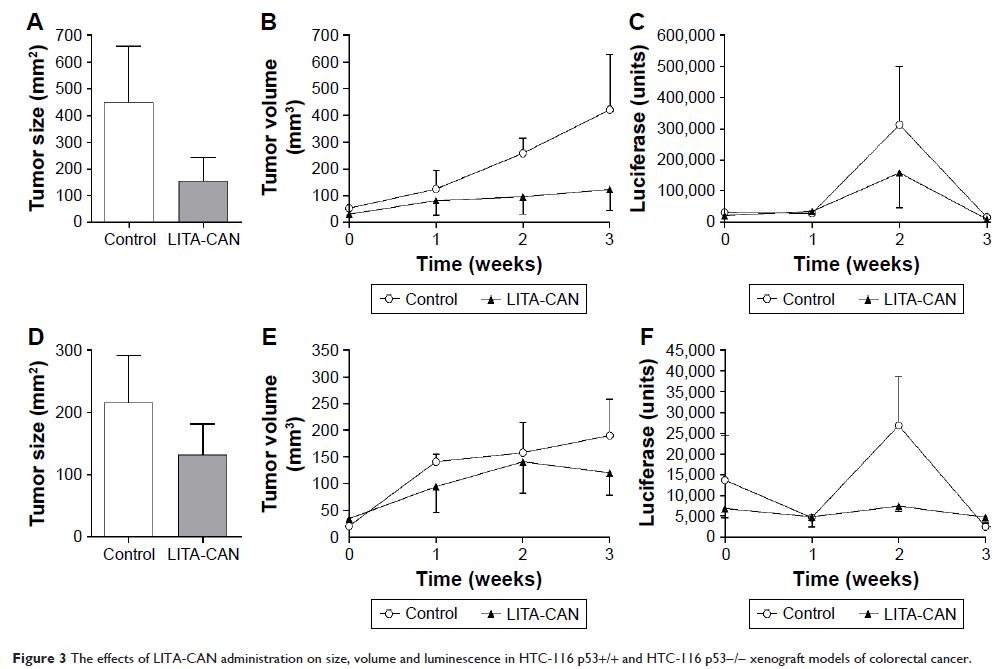
We assessed chronic in vivo administration of our nanoparticle in three
separate murine models of colorectal cancer. We demonstrated a substantial
reduction in tumor growth in the xenograft model of colorectal cancer cell
lines HT-29, HCT-116 p53+/+ and HCT-116 p53-/-. Nanoparticle-induced reductions
in histone deacetylase gene expression indicated a potential mechanism for
these anti-proliferative effects. Together, these results indicated that
LITA-CAN could be used as an effective direct or adjunct therapy to treat
malignant transformation in vivo.
Keywords: lipid-based
nanoparticles, liposomes, cancer, short-chain fatty acids, epigenetics