110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
Cognitive and behavioral evaluation of nutritional interventions in rodent models of brain aging and dementia
Authors Wahl D, Coogan SCP, Solon-Biet SM, de Cabo R, Haran JB, Raubenheimer D, Cogger VC, Mattson MP, Simpson SJ, Le Couteur DG
Received 30 June 2017
Accepted for publication 22 July 2017
Published 8 September 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1419—1428
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S145247
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Walker
Abstract: Evaluation of
behavior and cognition in rodent models underpins mechanistic and
interventional studies of brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases,
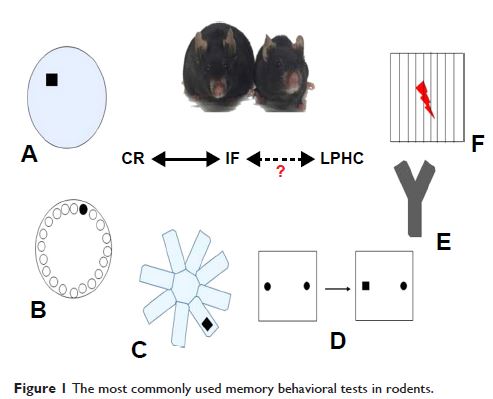
especially dementia. Commonly used tests include Morris water maze, Barnes
maze, object recognition, fear conditioning, radial arm water maze, and Y
maze. Each of these tests reflects some aspects of human memory including
episodic memory, recognition memory, semantic memory, spatial memory, and
emotional memory. Although most interventional studies in rodent models of
dementia have focused on pharmacological agents, there are an increasing number
of studies that have evaluated nutritional interventions including caloric
restriction, intermittent fasting, and manipulation of macronutrients. Dietary
interventions have been shown to influence various cognitive and behavioral
tests in rodents indicating that nutrition can influence brain aging and
possibly neurodegeneration.
Keywords: calorie restriction, intermittent fasting, aging, memory, macronutrients
Keywords: calorie restriction, intermittent fasting, aging, memory, macronutrients