110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

磷酸肌醇 3-激酶的靶向抑制会损害结肠癌细胞增殖、存活和侵袭
Authors Yang F, Gao JY, Chen H, Du ZH, Zhang XQ, Gao W
Received 5 July 2017
Accepted for publication 28 August 2017
Published 11 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4413—4422
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S145601
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: Colon
cancer is the third most common cancer in the world, and its metastasis and
drug resistance are challenging for its effective treatment. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of colon cancer. The aim of
this study was to investigate the targeting of PI3K in colon cancer cells HT-29
and HCT-116 in vitro.
Methods: In HT-29 and HCT-116 cells, BEZ235, a dual inhibitor of PI3K/mTOR, and
shRNAtarget to PI3KCA were used to inhibit PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. The
inhibition efficiency of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway was detected by RT-PCR and
Western blot. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis were
evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8, Transwell, and flow cytometry assays. The
expression of apoptosis-related proteins (cleavage caspase 3, Bcl-2, Bax, and
Bim) were also detected.
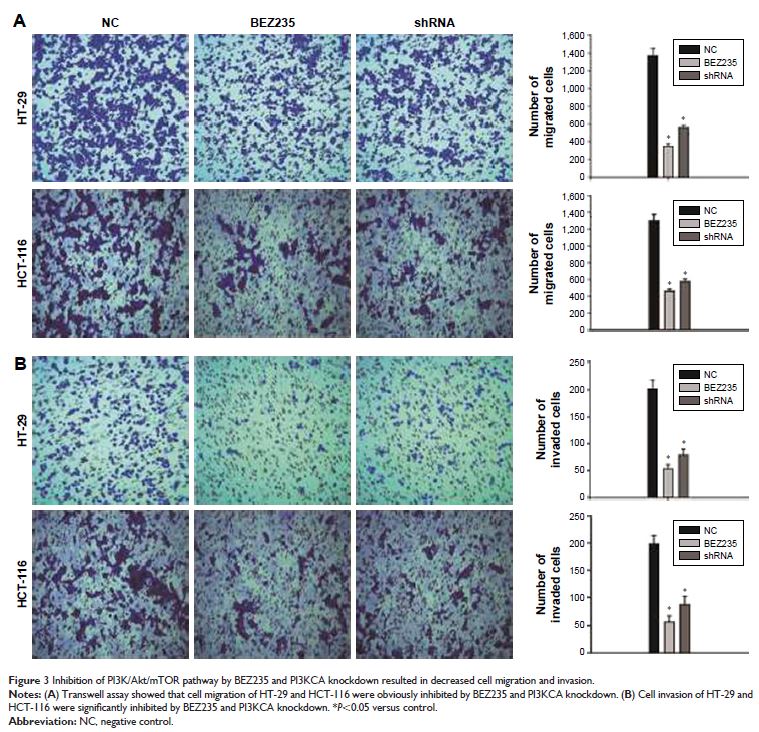
Results: We found that in HT-29 and HCT-116 cells, the treatment of BEZ235 (1 µM)
and PI3KCA knockdown inhibited the activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and
significantly suppressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of HT-29
and HCT-116 cells. In addition, we confirmed that knockdown of BEZ235 and
PI3KCA induced cell apoptosis through the upregulated levels of cleavage
caspase 3 and Bax and downregulated expression of Bcl-2 and Bim.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that targeted inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway impaired cell proliferation, survival, and invasion in human colon
cancer.
Keywords: human colon cancer, PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, BEZ235, PI3KCA knockdown