110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

乳腺癌预后免疫相关基因模型:一项汇总分析
Authors Zhao J, Wang Y, Lao Z, Liang S, Hou J, Yu Y, Yao H, You N, Chen K
Received 14 June 2017
Accepted for publication 3 August 2017
Published 11 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4423—4433
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S144015
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Abstract: Breast cancer, the most common cancer among women, is a clinically
and biologically heterogeneous disease. Numerous prognostic tools have been proposed,
including gene signatures. Unlike proliferation-related prognostic gene
signatures, many immune-related gene signatures have emerged as principal
biology-driven predictors of breast cancer. Diverse statistical methods and
data sets were used for building these immune-related prognostic models, making
it difficult to compare or use them in clinically meaningful ways. This study
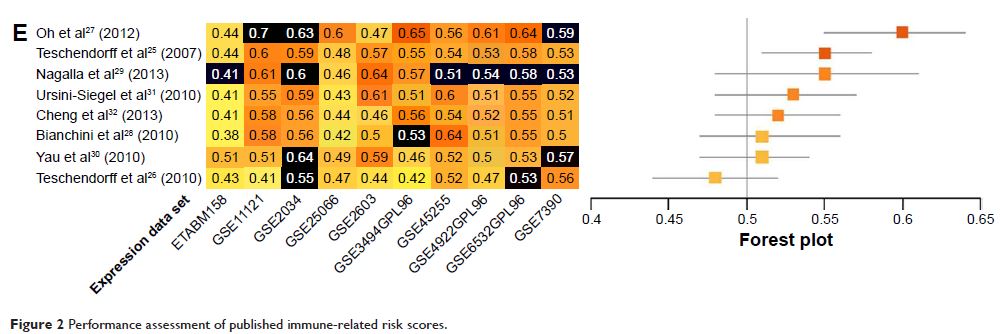
evaluated successfully published immune-related prognostic gene signatures
through systematic validations of publicly available data sets. Eight
prognostic models that were built upon immune-related gene signatures were
evaluated. The performances of these models were compared and ranked in ten
publicly available data sets, comprising a total of 2,449 breast cancer cases.
Predictive accuracies were measured as concordance indices (C-indices). All
tests of statistical significance were two-sided. Immune-related gene models
performed better in estrogen receptor-negative (ER-) and lymph node-positive
(LN+) breast cancer subtypes. The three top-ranked ER- breast cancer models
achieved overall C-indices of 0.62–0.63. Two models predicted better than
chance for ER+ breast cancer, with C-indices of 0.53 and 0.59, respectively.
For LN+ breast cancer, four models showed predictive advantage, with C-indices
between 0.56 and 0.61. Predicted prognostic values were positively correlated
with ER status when evaluated using univariate analyses in most of the models
under investigation. Multivariate analyses indicated that prognostic values of the
three models were independent of known clinical prognostic factors.
Collectively, these analyses provided a comprehensive evaluation of
immune-related prognostic gene signatures. By synthesizing C-indices in
multiple independent data sets, immune-related gene signatures were ranked for
ER+, ER-, LN+, and LN- breast cancer subtypes. Taken together, these data
showed that immune-related gene signatures have good prognostic values in
breast cancer, especially for ER- and LN+ tumors.
Keywords: breast cancer,
prognostic models, immune-related gene