111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

microRNA-20a 在人多发性骨髓瘤中的致癌作用
Authors Wang T, Tao W, Zhang L, Li SL
Received 9 June 2017
Accepted for publication 3 August 2017
Published 11 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4465—4474
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143612
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
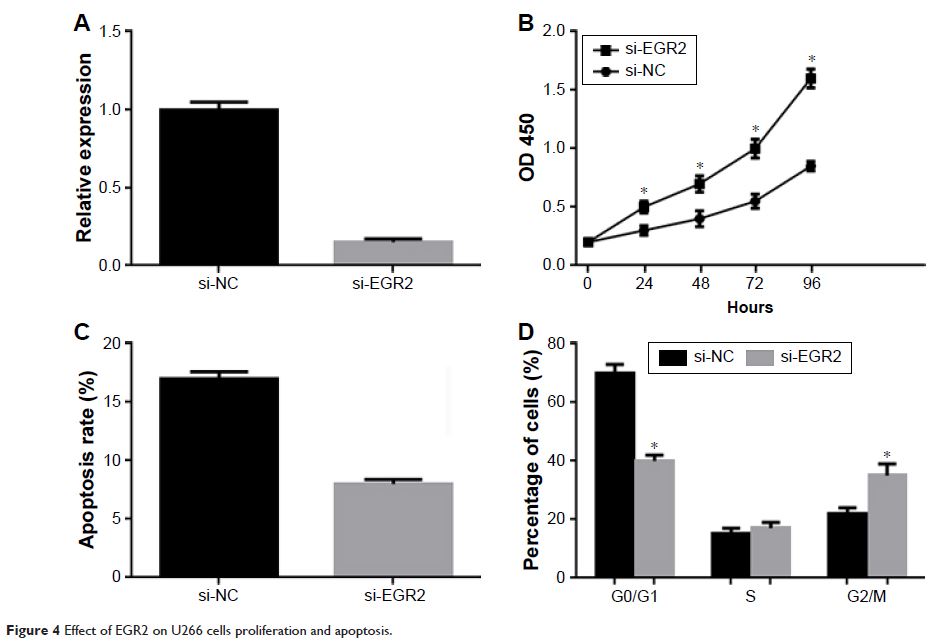
Abstract: microRNAs are important in cancer biogenesis and development. However,
their underlying mechanisms in multiple myeloma (MM) are barely characterized.
microRNA-20a (miR-20a) is a member of the microRNA-17-92 cluster. It has been
implicated in various cancers, regulating the proliferation and invasion of
cancer cells in vitro. Compared with healthy donors, it also has been reported
to be elevated in plasma of MM patients. Here, we investigated the function of
miR-20a. Our results showed that it promotes proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis of MM cells in vitro by inhibiting early growth response protein 2.
The effects of miR-20a were also evaluated in MM xenograft models of SCID/NOD
mice. Apparent antitumor activity was achieved in xenograft mice injected with
miR-20a inhibitor, while mimics of miR-20a significantly promoted tumor growth.
These data indicate that miR-20a plays a crucial role in the biology of MM and
represents a potential target for novel therapies for MM patients.
Keywords: miR-20a, EGR2,
multiple myeloma