111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

透明质酸官能化铋系氧化物纳米粒子用于计算机断层扫描成像引导下的肿瘤放射治疗
Authors Du FY, Lou JM, Jiang R, Fang ZZ, Zhao XF, Niu YY, Zou SQ, Zhang MM, Gong AH, Wu CY
Received 16 December 2016
Accepted for publication 8 May 2017
Published 21 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5973—5992
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S130455
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
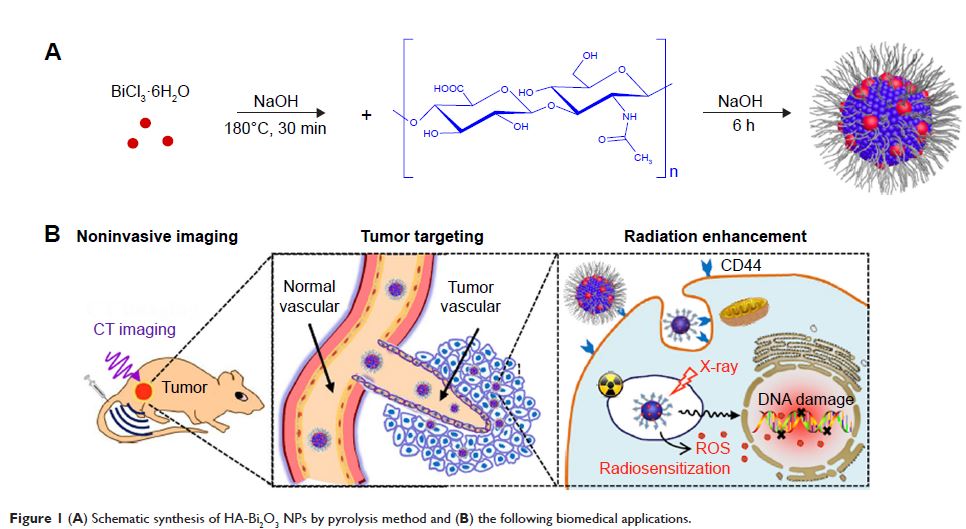
Abstract: The inherent radioresistance and inaccuracy of localization of
tumors weaken the clinical implementation effectiveness of radiotherapy. To
overcome these limitations, hyaluronic acid-functionalized bismuth oxide
nanoparticles (HA-Bi2O3 NPs) were
synthesized by one-pot hydrothermal method for target-specific computed
tomography (CT) imaging and radiosensitization of tumor. After
functionalization with hyaluronic acid, the Bi2O3 NPs possessed favorable solubility in water
and excellent biocompatibility and were uptaken specifically by cancer cells
overexpressing CD44 receptors. The as-prepared HA-Bi2O3 NPs
exhibited high X-ray attenuation efficiency and ideal radiosensitivity via
synergizing X-rays to induce cell apoptosis and arrest the cell cycle in a
dose-dependent manner in vitro. Remarkably, these properties offered excellent
performance in active-targeting CT imaging and enhancement of radiosensitivity
for inhibition of tumor growth. These findings demonstrated that HA-Bi2O3 NPs as
theranostic agents exhibit great promise for CT imaging-guided radiotherapy in
diagnosis and treatment of tumors.
Keywords: HA-Bi2O3 NPs, CT
imaging, radiosensitivity, HA, bismuth