111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

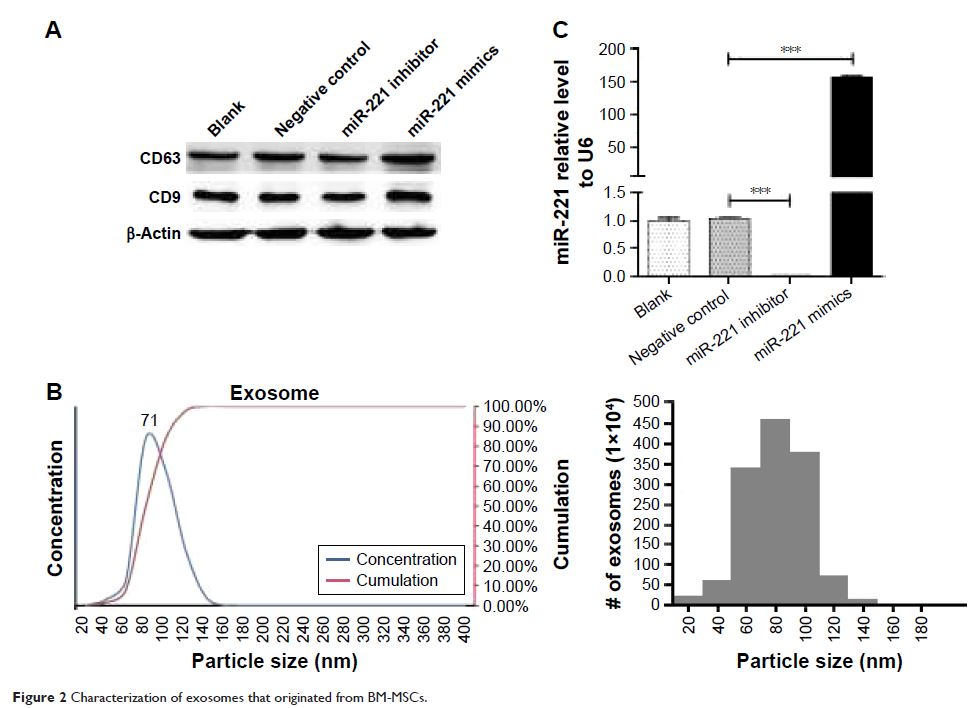
源自骨髓间充质干细胞的外来体的 miRNA-221 可促进胃癌中的致癌活性
Authors Ma M, Chen S, Liu Z, Xie H, Deng H, Shang S, Wang X, Xia M, Zuo C
Received 6 June 2017
Accepted for publication 20 July 2017
Published 22 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4161—4171
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143315
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Abstract: Worldwide, gastric cancer (GC) is one of the deadliest malignant tumors
of the digestive system. Moreover, microRNAs (miRNAs) of exosomes harbored
within cancer cells have been determined to induce inflammatory conditions that
accelerate tumor growth and metastasis. Interestingly, the oncogenic role of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) in the modulation of
immunosuppression, tumor invasion, and metastasis was discovered to be partly
mediated through the secretion of exosomes. In this article, high expression of
miRNA-221 (miR-221) in exosomes of the peripheral blood was determined to be
positively correlated with the poor clinical prognosis of GC, especially with
respect to tumor, node, and metastases stage. Therefore, the expression of
miR-221 in exosomes of the peripheral blood may be an important detection index
for GC. Proliferation, migration, invasion, and adhesion to the matrix of GC
BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells were significantly enhanced by exosomes that
originated from BM-MSCs that were transfected with miR-221 mimics. In
conclusion, extracted exosomes from BM-MSCs transfected with miR-221
oligonucleotides can act as high-efficiency nanocarriers, which can provide
sufficient miR-221 oligonucleotides to influence the tumor microenvironment and
tumor aggressiveness effectively. Notably, the use of a miR-221 inhibitor with
an excellent restraining effect in exosomes provides therapeutic potential for
GC in future clinical medicine.
Keywords: exosomes,
miR-221, BM-MSCs, gastric cancer, prognosis, oncogenic activity